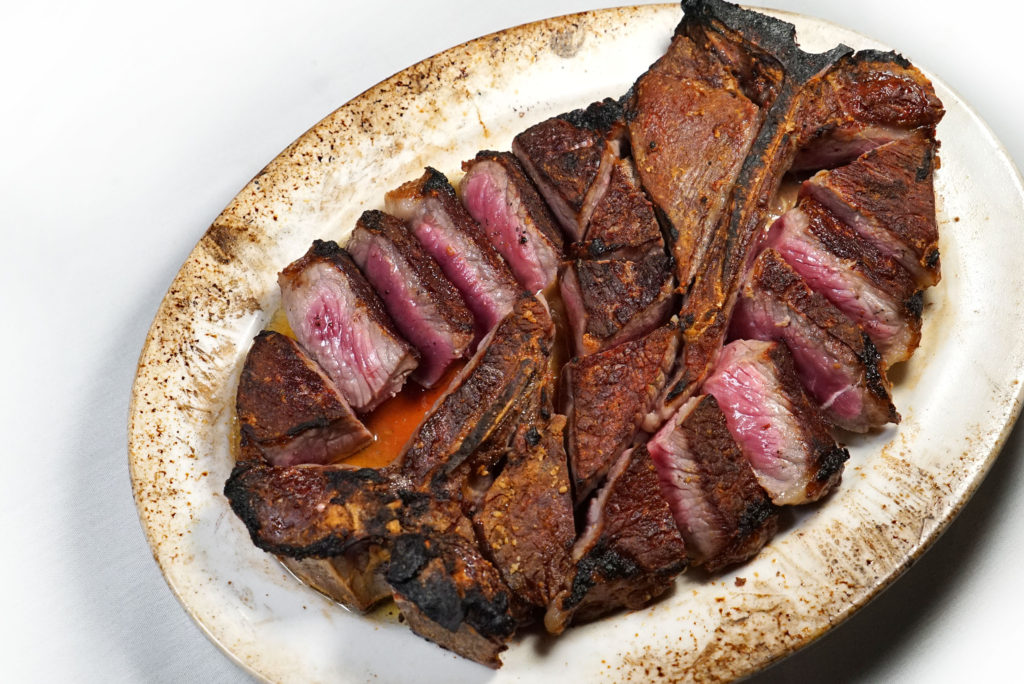
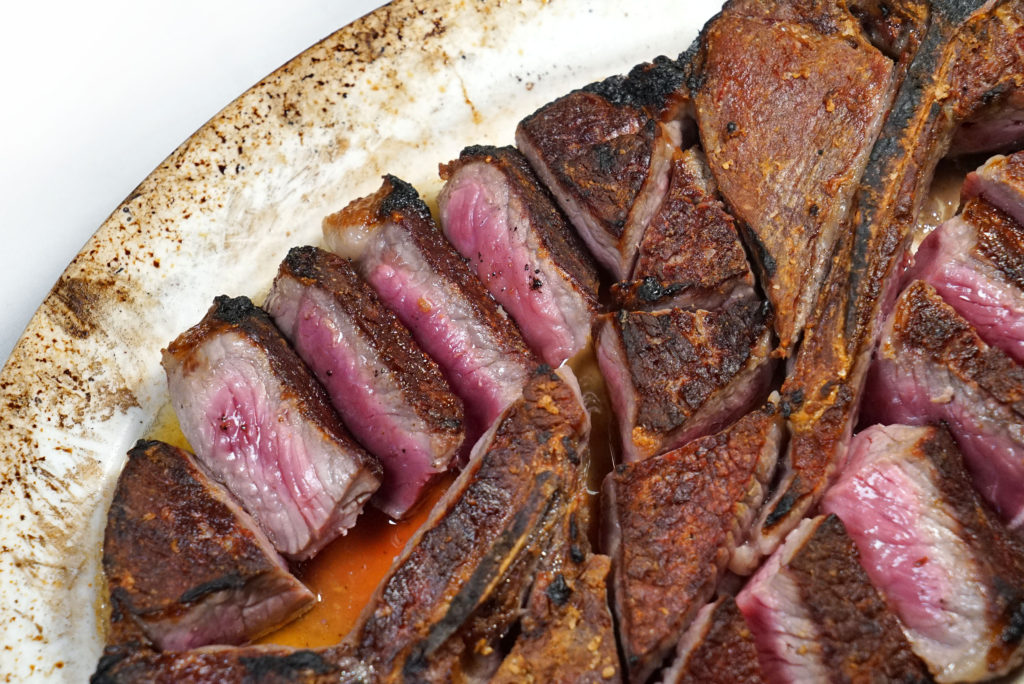
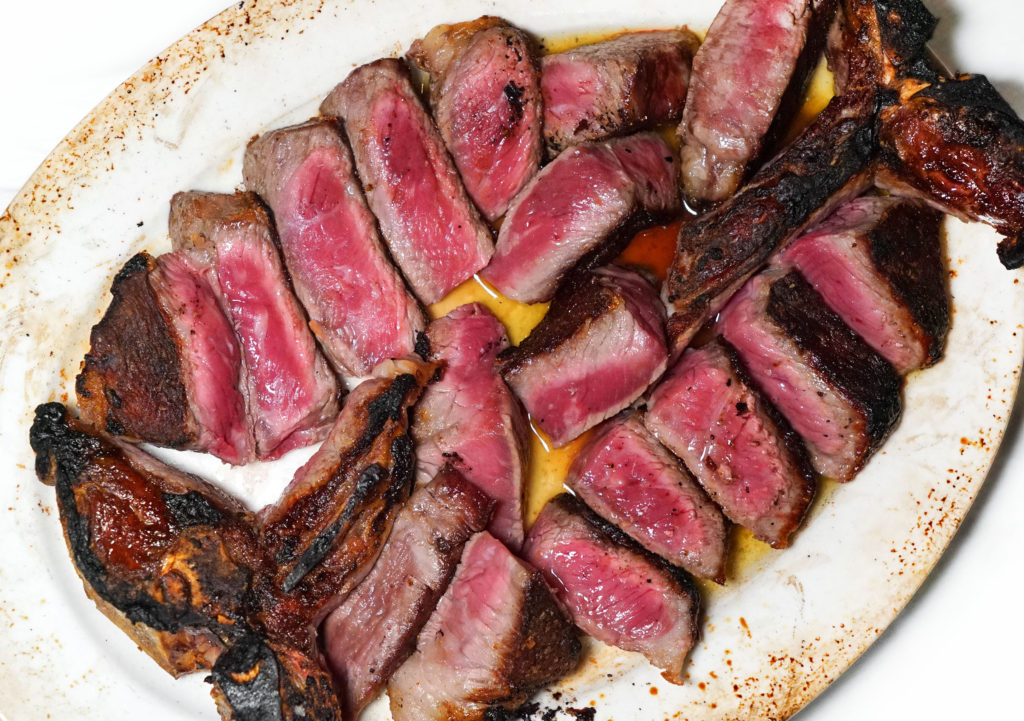
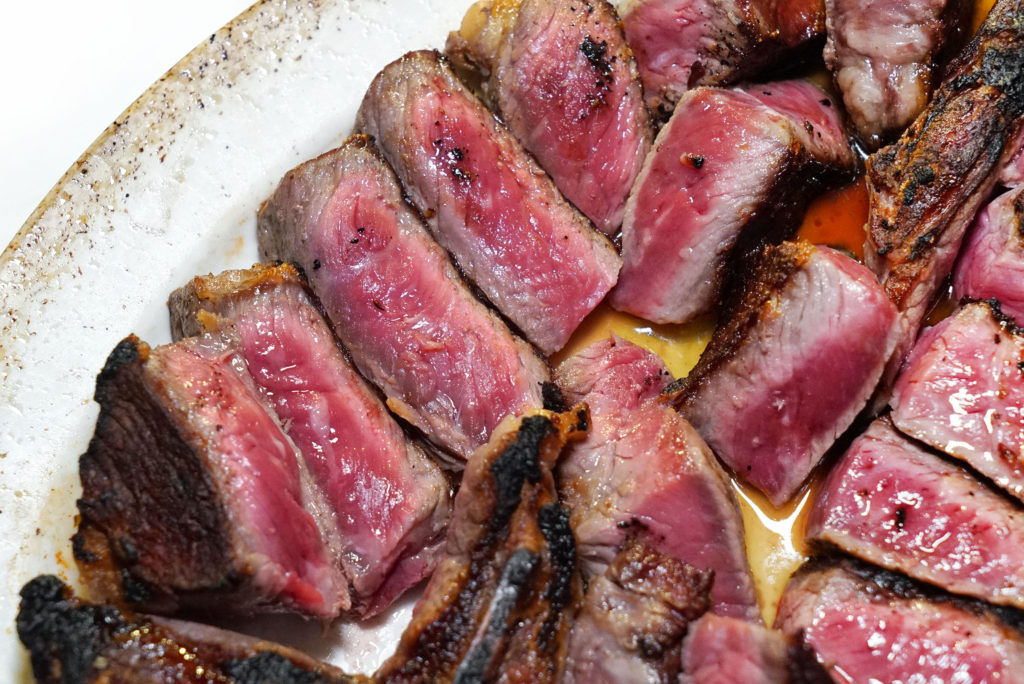
Like all great businesses, there’s usually a great story behind the success. Let’s take Strassburger Steaks, for example.

A girl brings her father a homemade sandwich to the family’s beef plant in the Bronx – I’m guessing roast beef with horseradish sauce on a nice crusty roll. There, she meets her future husband, who is working as her father’s right-hand man. Over 150 years later, that family still prides itself on the traditions of dedicated daughters and great steak.
Suzanne “Suzy Sirloin” Strassburger and her sister Andrea work with their father, who has passed down to them five generations of work ethic along with a successful and well-respected business. In the story above, the father is Suzy’s great-great grandfather, and the daughter is her great grandmother.
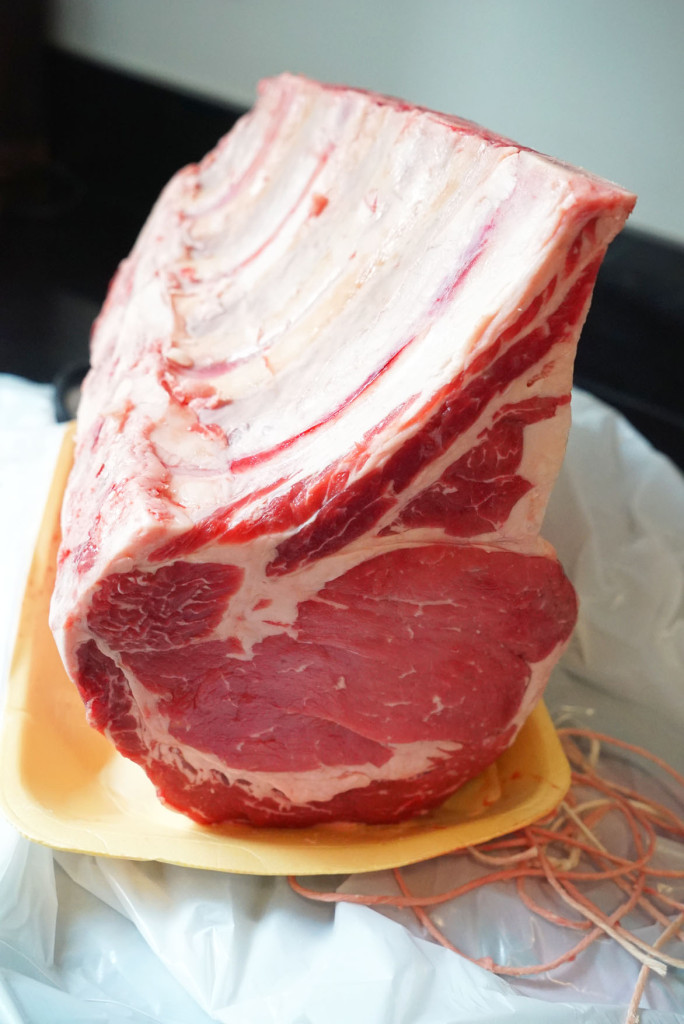
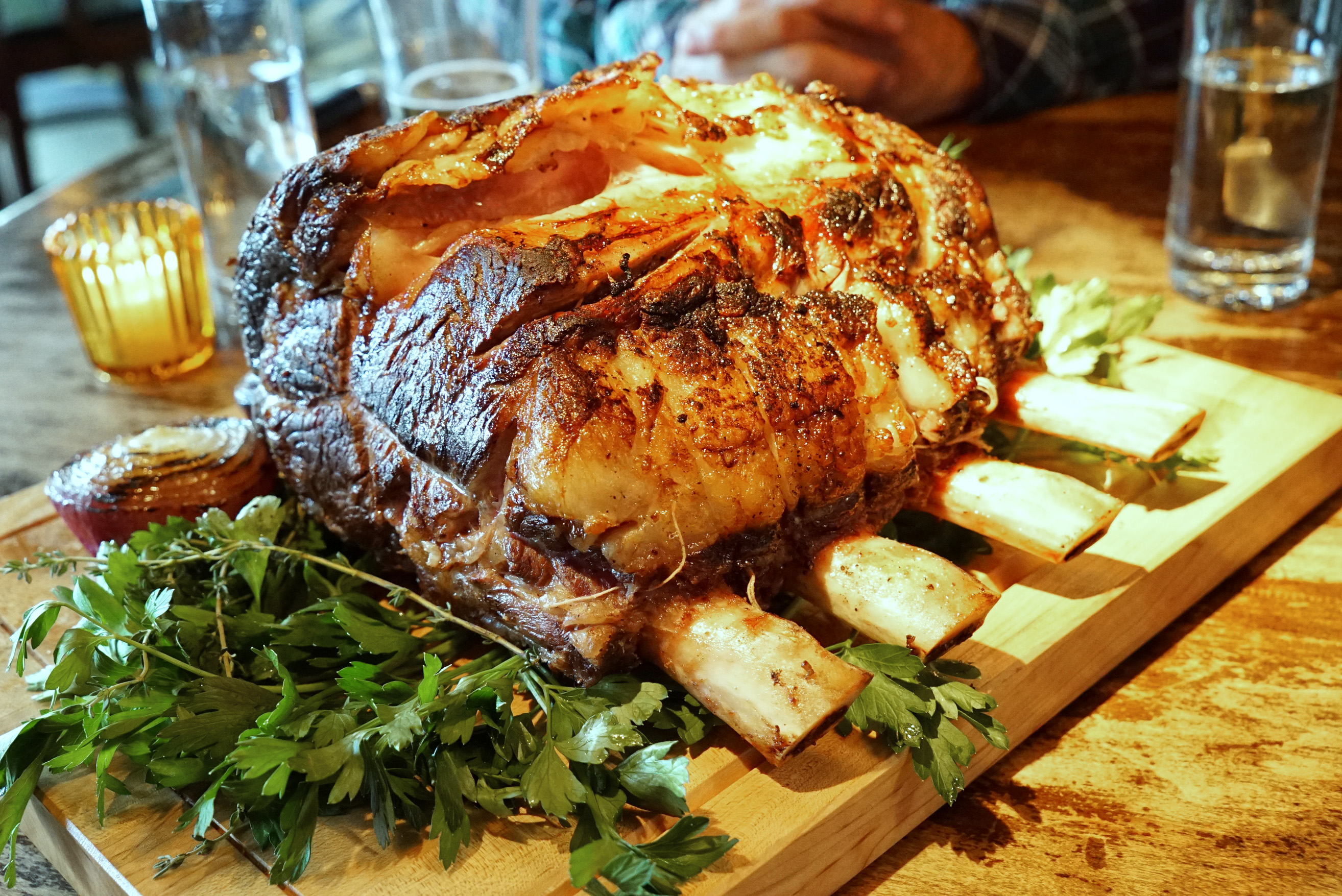
Suzy and Andrea’s own father, Peter “T-Bone” Strassburger, is an innovator and leader in the industry. He started boxed beef in New York (wholesale cuts of beef, like rib and loin, individually packaged and placed into boxes for shipping), and he educated many steakhouses on the virtues of aged beef. In fact, his family was the first to install an aging room in their plant.
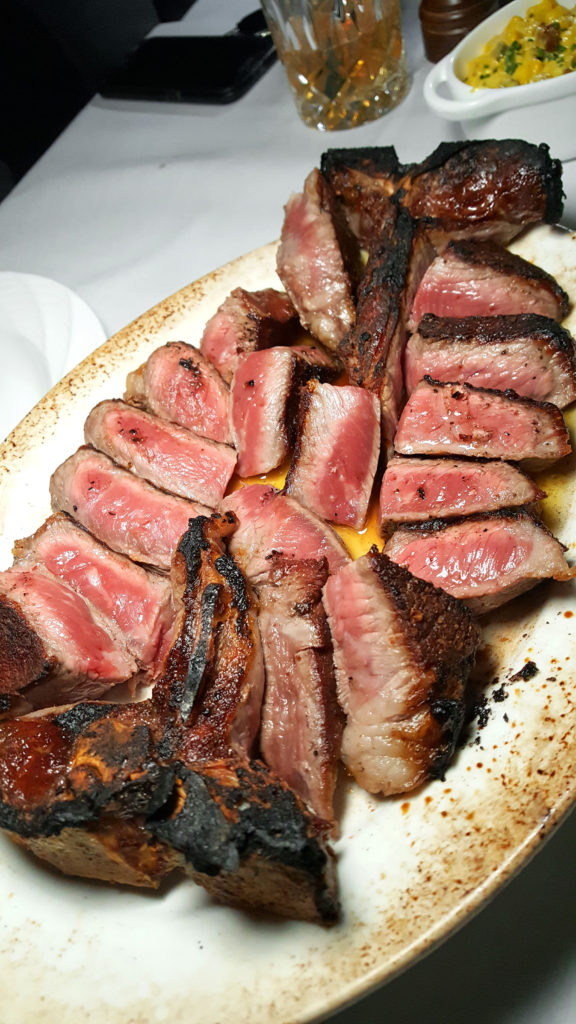
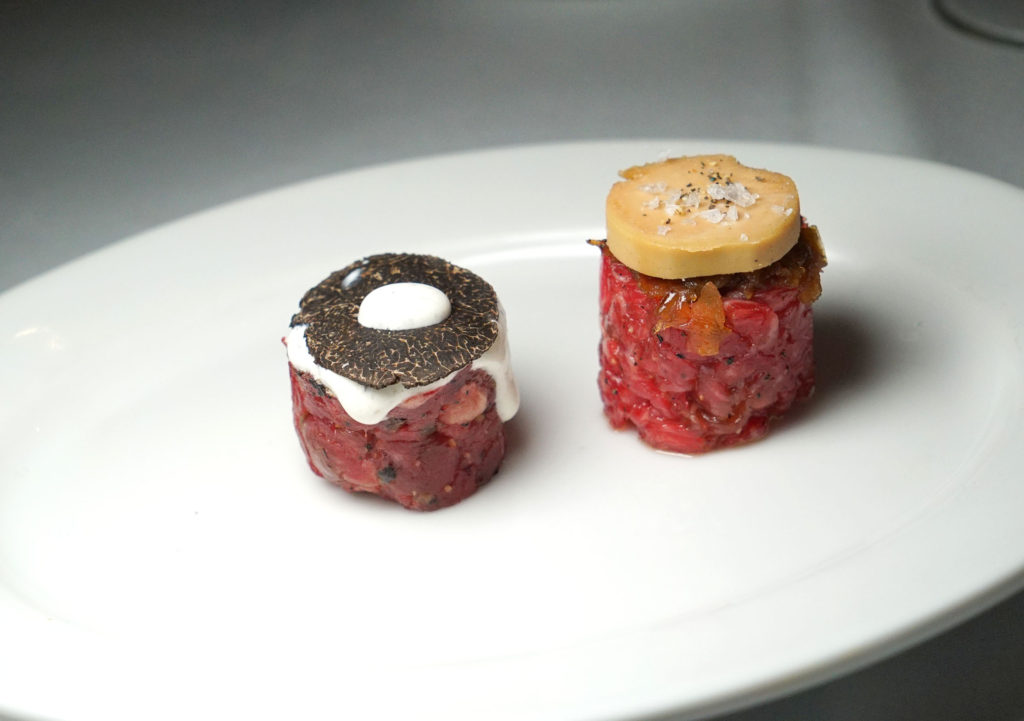
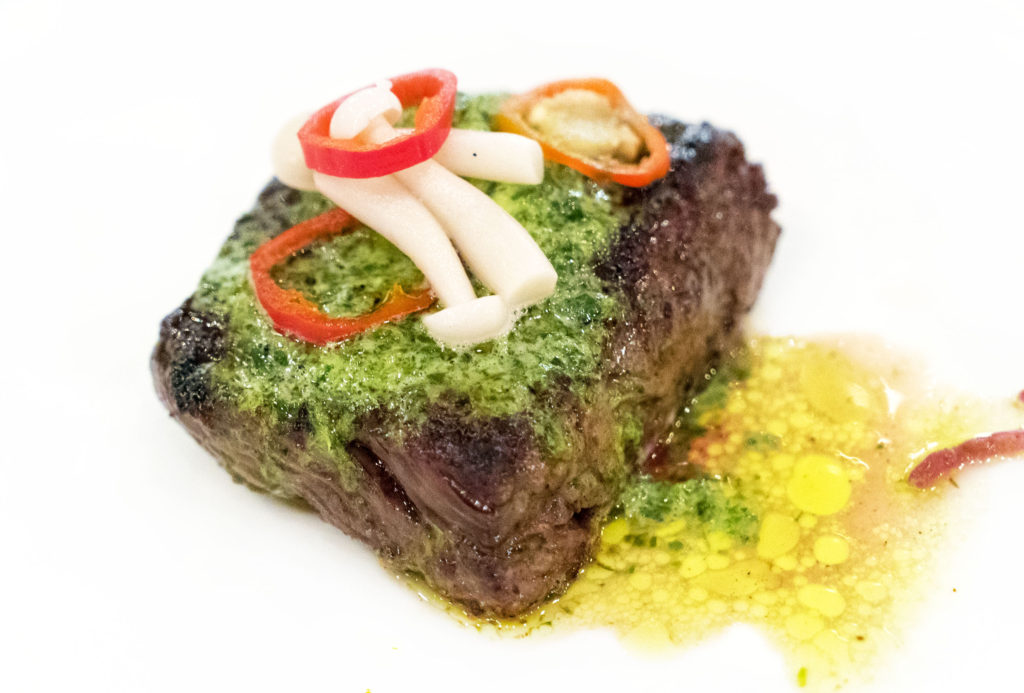
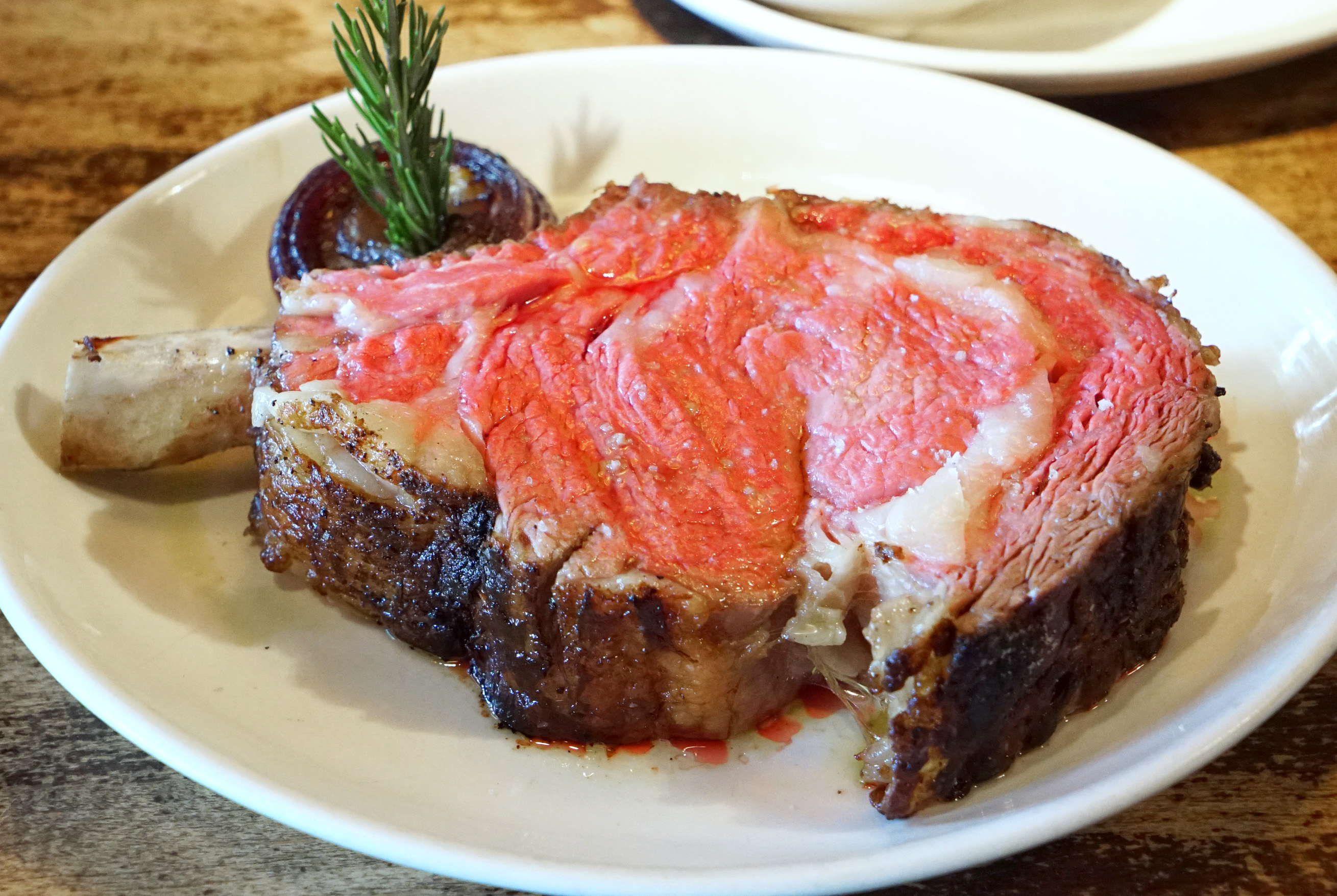
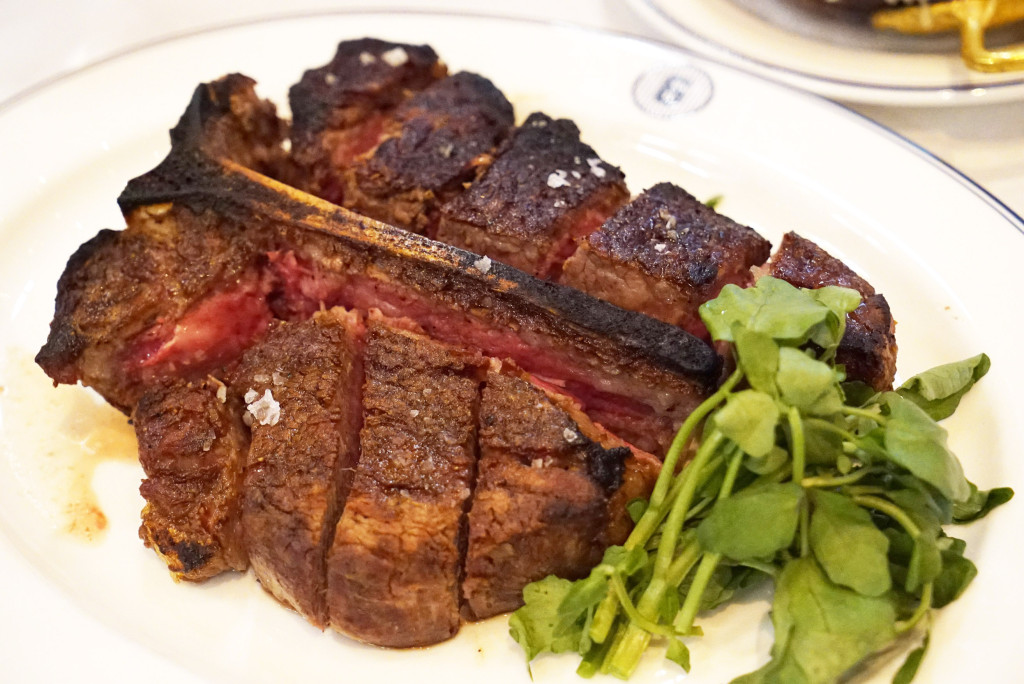
Strassburger is no joke when it comes to quality. The company supplies meat to several of my top ranked steakhouses, including Angus Club, Keen’s, Quality Italian and Quality Meats. You may have seen the name gracing menus all over the place. Their brand is worth featuring.

But in addition to supplying prime, dry-aged beef to high-end NYC restaurants, Strassburger also sells steaks online at the consumer level. And now Suzanne is also promoting her brand “Suzy Sirloin” to grocery stores around the city. With this venture, she is moving pork and all natural, hormone-free beef as a way to diversify. Smart!

She has a knack for marketing, too. It’s not often you see a woman walking around Manhattan in a big straw cowboy hat, but that’s Suzy’s signature accessory, and it’s even featured as part of her “Suzy Sirloin” logo.
She has said that she wears the hat as a sign of respect to all the hard working ranchers that produce the beef she sells. Right on! I can get on board with that.

Suzy is also a fellow Masters of Beef Advocacy graduate and Top of the Class trainee, like me, so we both like to blab about the benefits of beef, both for society in general and as part of a well-balanced and nutritious diet. You can check out her blog here, but she also founded The Sirloin Report, to which I’ve linked in the past.
I had a chance to interview her on the phone. We started from a string of 10 questions, and chatted from there. Read on below and enjoy! I’ve done my best to distill our conversations down to all the best bits of information.
1) When did you realize you wanted to work in the meat business? Was it something you always knew you wanted to do, or did it take some time to grow on you?
I knew immediately that I wanted to work in the business from the age of three or four. I always thought it was cool that when I asked my dad what he did, he’d respond that he worked for Poppa [Suzy’s grandfather]. Any day off that I had from school, I would be at the family meat factory helping out, answering phones, anything I could do.
Suzy went to college and started working professionally at the company around age 24. She worked literally every job in the business; putting together boxes, packing the boxes, you name it. This allowed her to really understand the challenges faced by each employee. She even worked beside guys in the cooler who had been there since her grandfather was running the place.
Suzy talked a lot about her family’s five and six generations in the meat business (both of her dad’s parents had beef industry families), and a lot about her dad.
Suzy has had some great success, but she says that her dad is a tough act to follow. He had eight plants out west that produced 10 million pounds of beef per week. He was the first wholesaler to box beef and to dry age beef in NYC. He’s still working today at 78 years old, and he always encourages Suzy and her sister to work hard and keep learning. In fact, Suzy went back to school this year and is enrolled in a program at Harvard business school. She’s always staying current and continuing to learn.
2) What is a typical day of work like for you from start to finish?
My work changes from day to day depending on where the business needs me. Some days I’ll be buying, other days selling. I’m also the business’ problem solver, so I have to make sure that everything is coming together and running smoothly.
3) What are some of the challenges and rewards you experience working in this business?
While the work was more challenging when I was younger, assembling the right team and having the right people around really helped. My sister runs the most challenging aspect of the business, which is collections. As for the most rewarding aspect? Enjoying a delicious steak at a client’s establishment.
4) I know you supply one of my favorite restaurants, Keens, with its beef. Do you also supply them with their legendary mutton?
Suzy does not supply Keen’s with their mutton. She deals exclusively in beef.
5) How do your foodservice clients choose their beef? Do they rely on your selection, or do they choose the cuts themselves?
Both. Some clients wish to choose everything, while others have developed long and trusting relationships with my family and rely on our expertise.
Suzy also explained that this loyalty and trust goes in the other direction too, from her to her beef suppliers. When times get tough and beef is hard to come by or expensive, Suzy has long standing relationships in place that allow her to still get her hands on the best supply.
6) Do you find that your clients and customers are well versed in beef nutrition, safety and the various niche labels, or is that something about which you constantly have to educate?
Suzy is constantly educating people about beef. She and I both went through the MBA and Top of the Class programs with the NCBA, so she, like me, is constantly providing useful information to people, both client and consumer alike. But there’s one thing she likes to say about food safety:
Buy it cold, serve it hot and keep it clean!
7) Is there a particular region of the country or breed of cattle from which you like to source your beef? I know food trends are pushing hard for “local” products, but doesn’t the best quality beef come from the Midwest and Texas?
Suzy supports ranchers and farmers from all over. She tries to make sure the client is happy. Whatever the client wants to serve at their restaurant, she will help to make it happen.
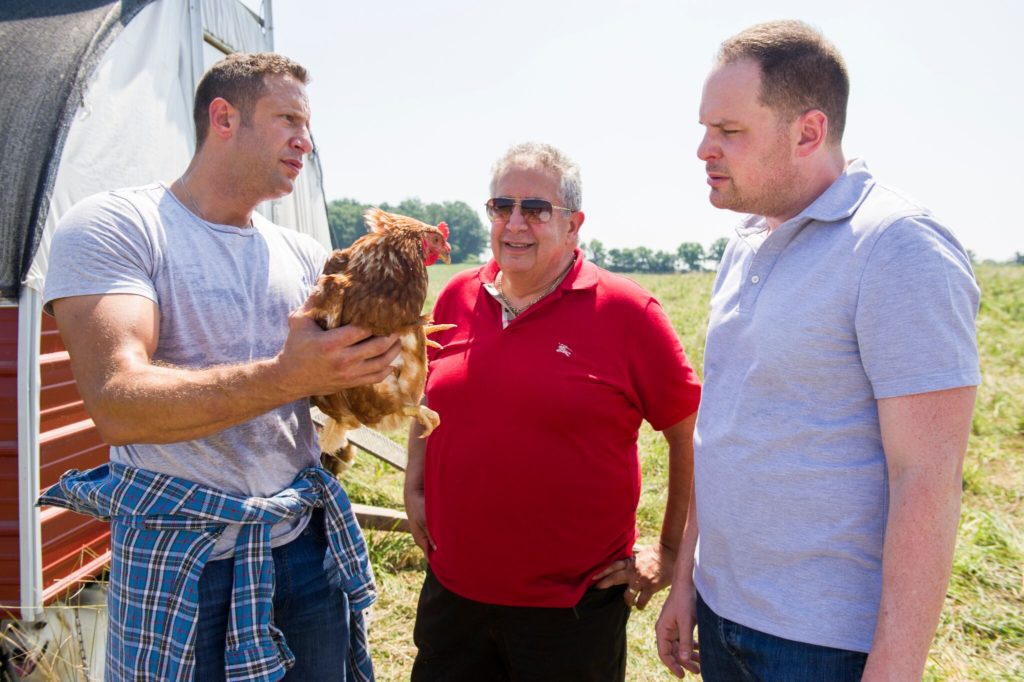
8) How often do you interact with farmers, ranchers, and other producers before the beef gets to your operation?
The reason Suzy wears her cowboy hat all the time is because she believes that beef and her business is ultimately all about the ranchers and farmers. She visits ranches and farms often, and many of her close friends are ranchers, farmers and butchers. She surrounds herself with people who are working with the animals daily. Not only does Suzy understand what goes into beef production, but she respects the process and doesn’t take for granted what these hard working families do for the American food supply.
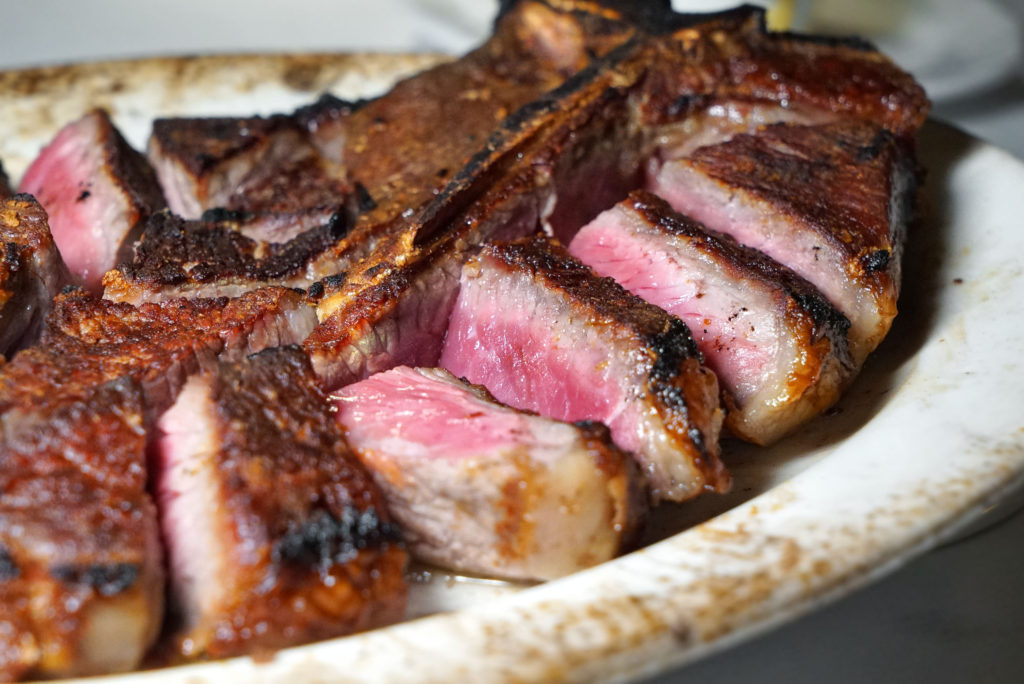
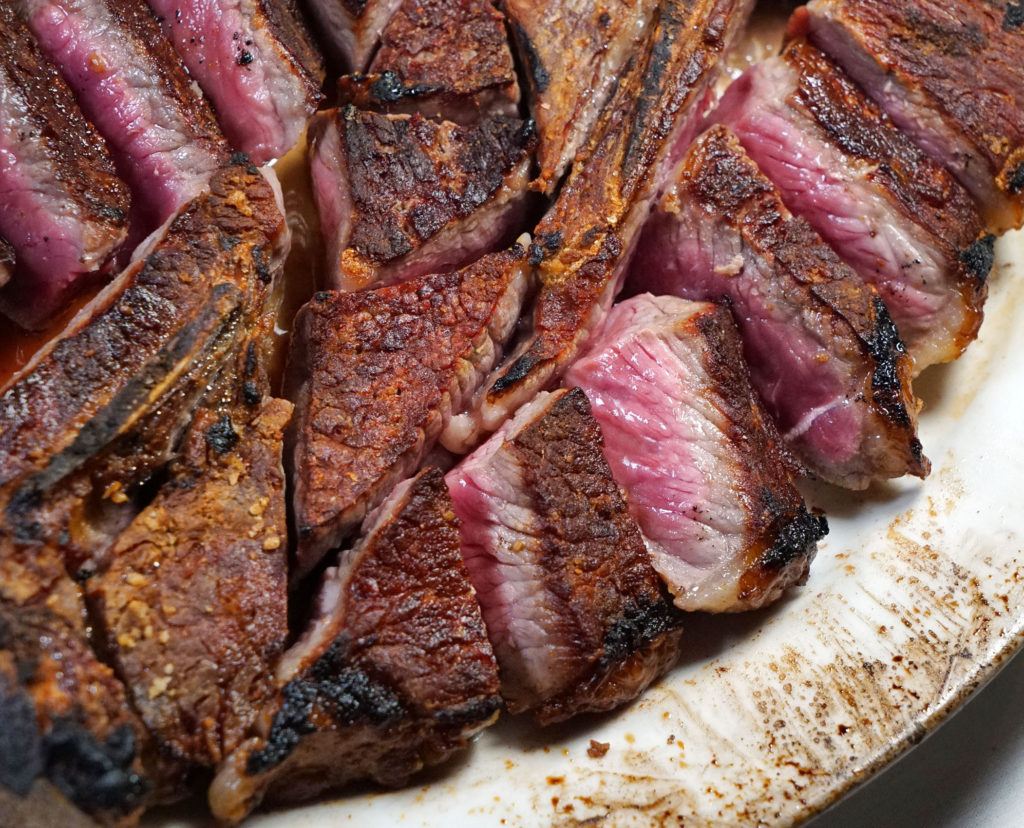
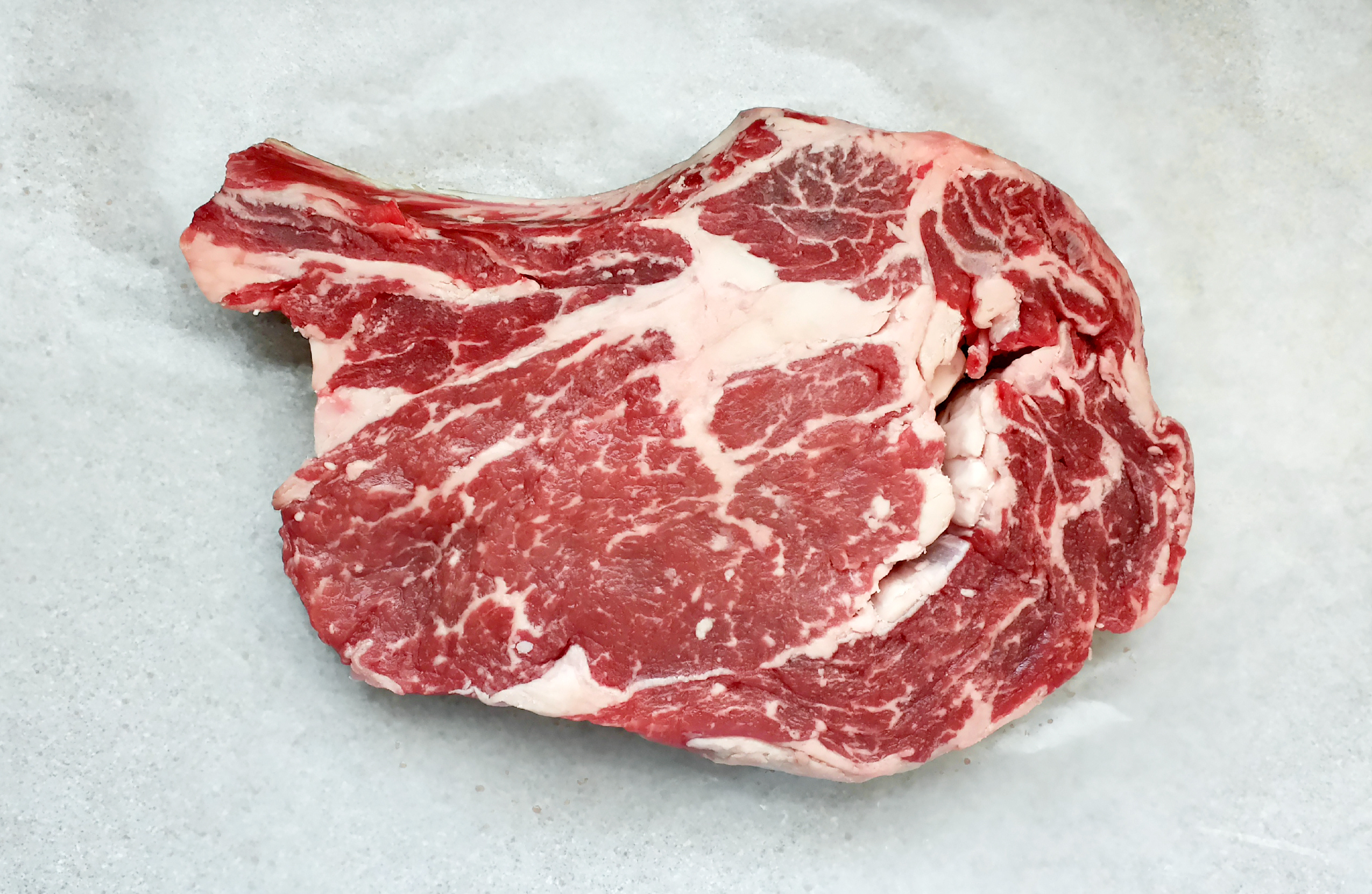
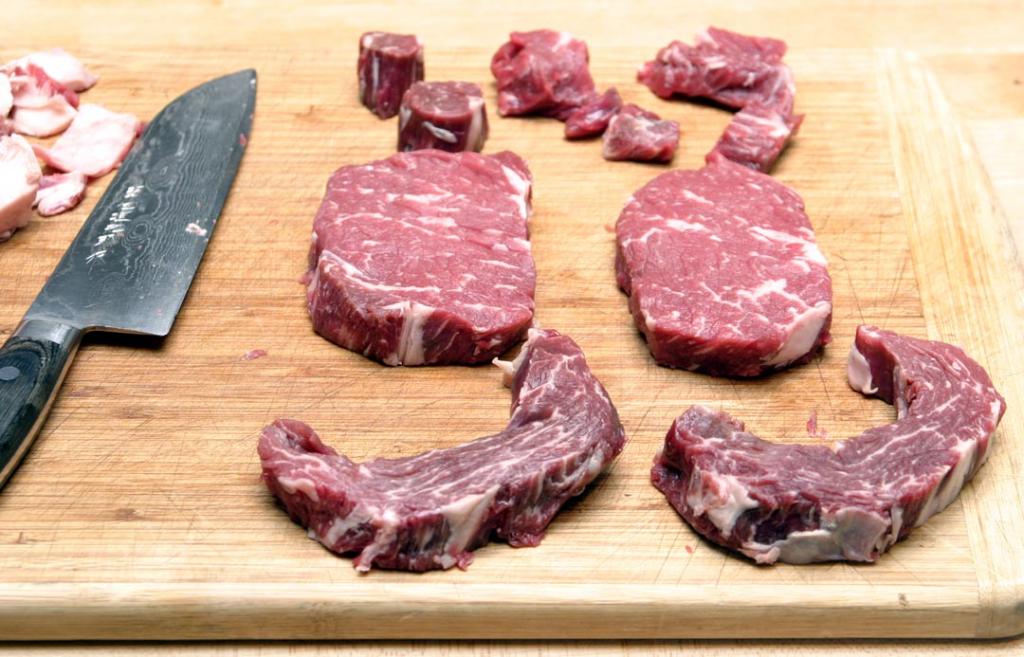
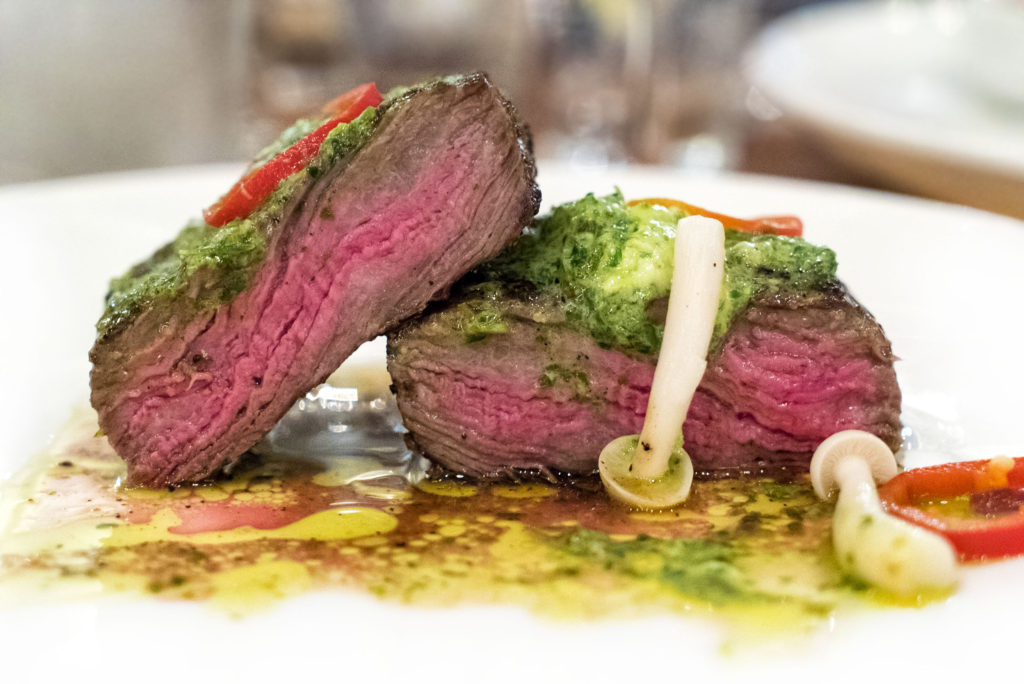
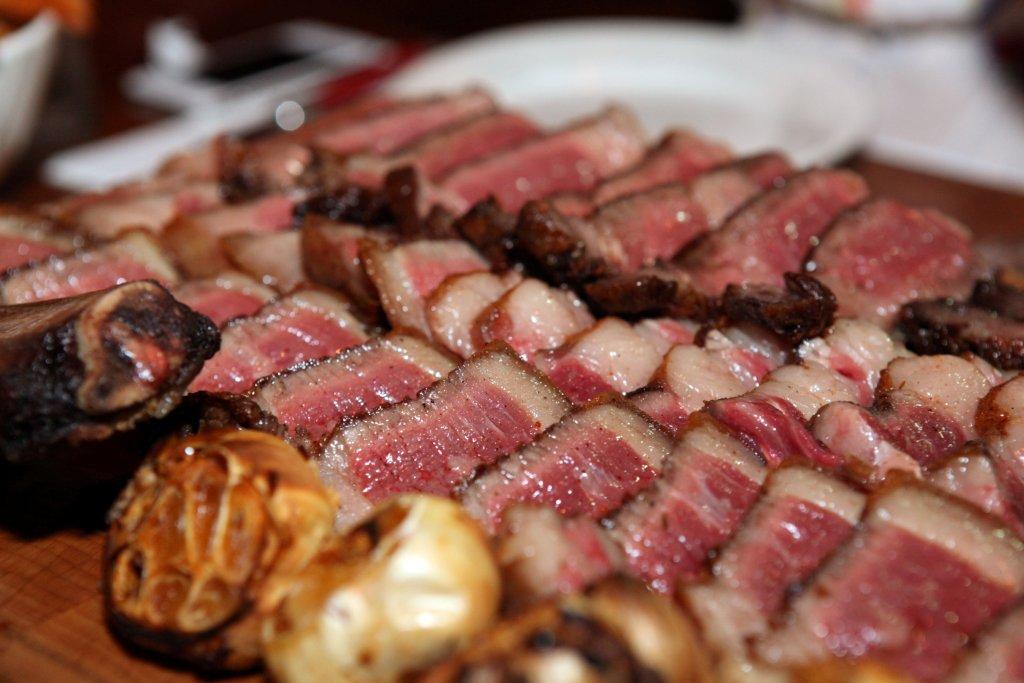
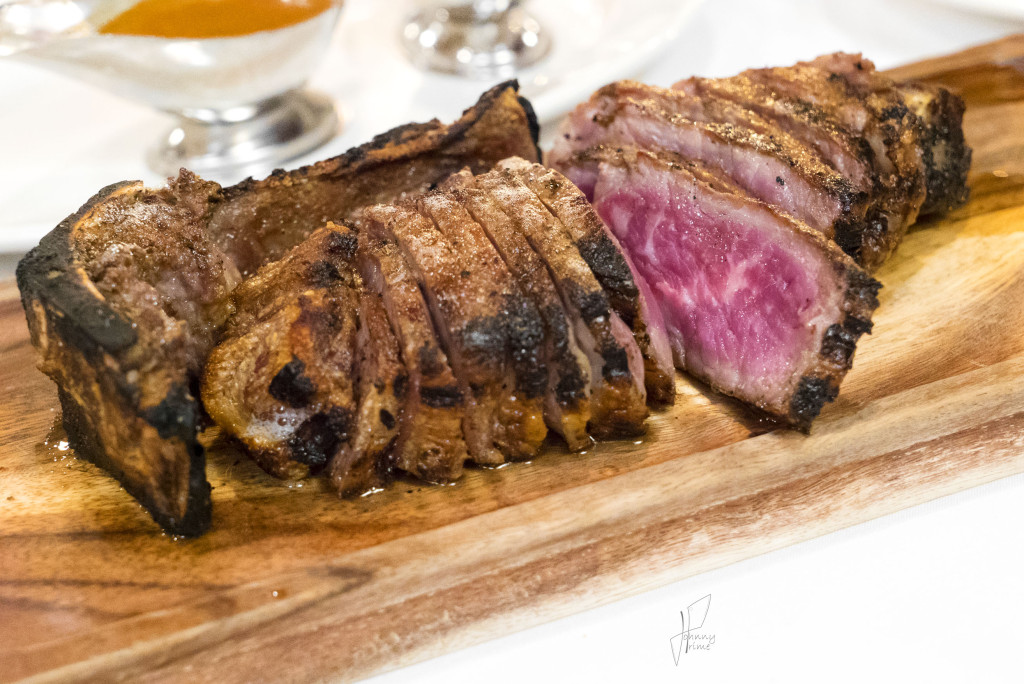
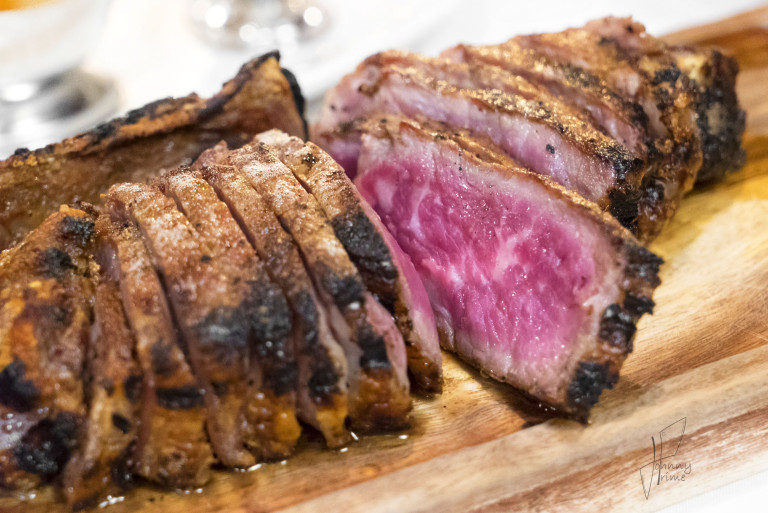
9) I’m a big fan of dry-aged beef. Do you find that any particular cuts take to this process better than others, and are there amounts of time that are too long or too short for producing good flavor?
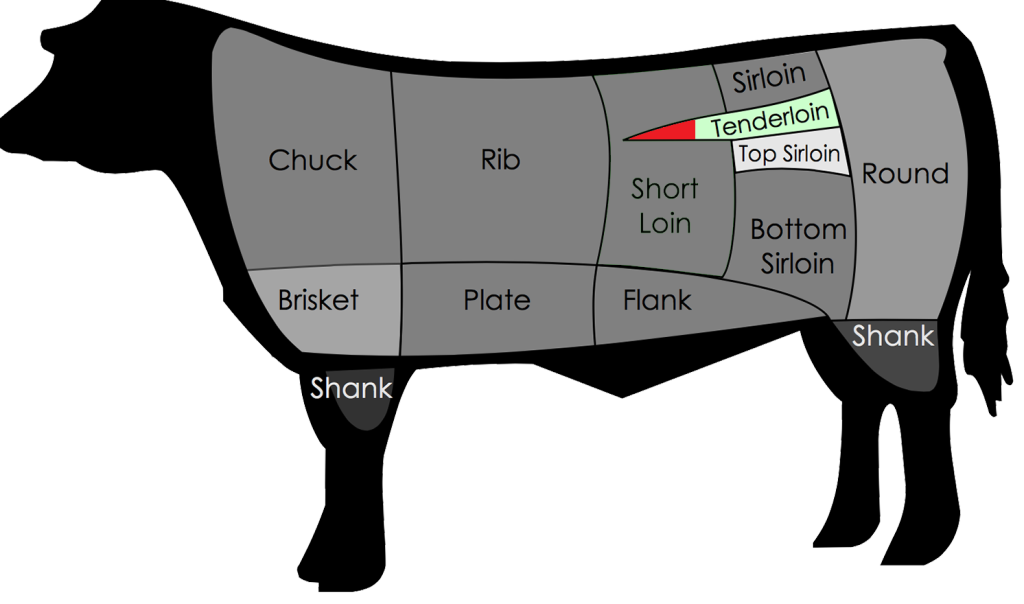
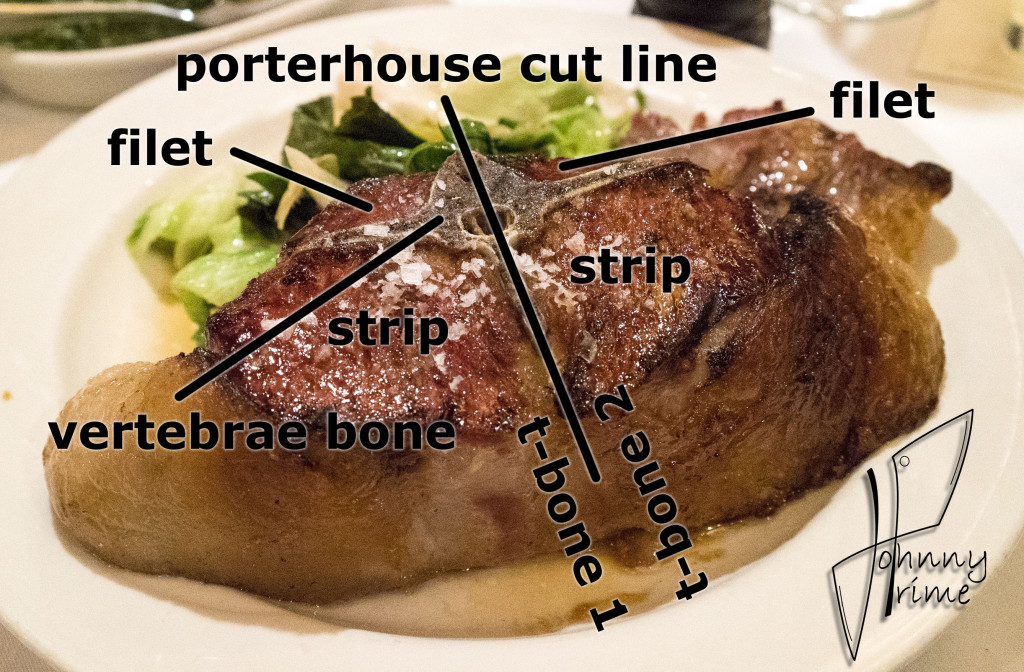
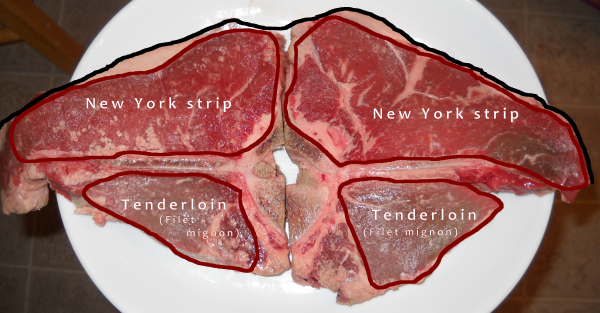
We dry age middle meats like shells [bone-in strip loins], short loins [porterhouses and t-bones], and ribs. We typically age them for three to four weeks, but it really depends on what the customer or client wants.
After we chatted for a bit about her family’s important role in the world of dry-aged beef, Suzy astutely pointed out that no two aging rooms are alike. The way the beef turns out all depends on how often people walk in and out of the room, the air circulation, the lighting, temperature, humidity, etc.
10) What’s your favorite cut of beef and why? Grilled, smoked, or seared in a pan? And how often do you eat beef in any given week?
A grilled, prime, boneless New York strip steak is my favorite. And I eat beef 14 times a week.
WOW! Now that’s impressive!!!