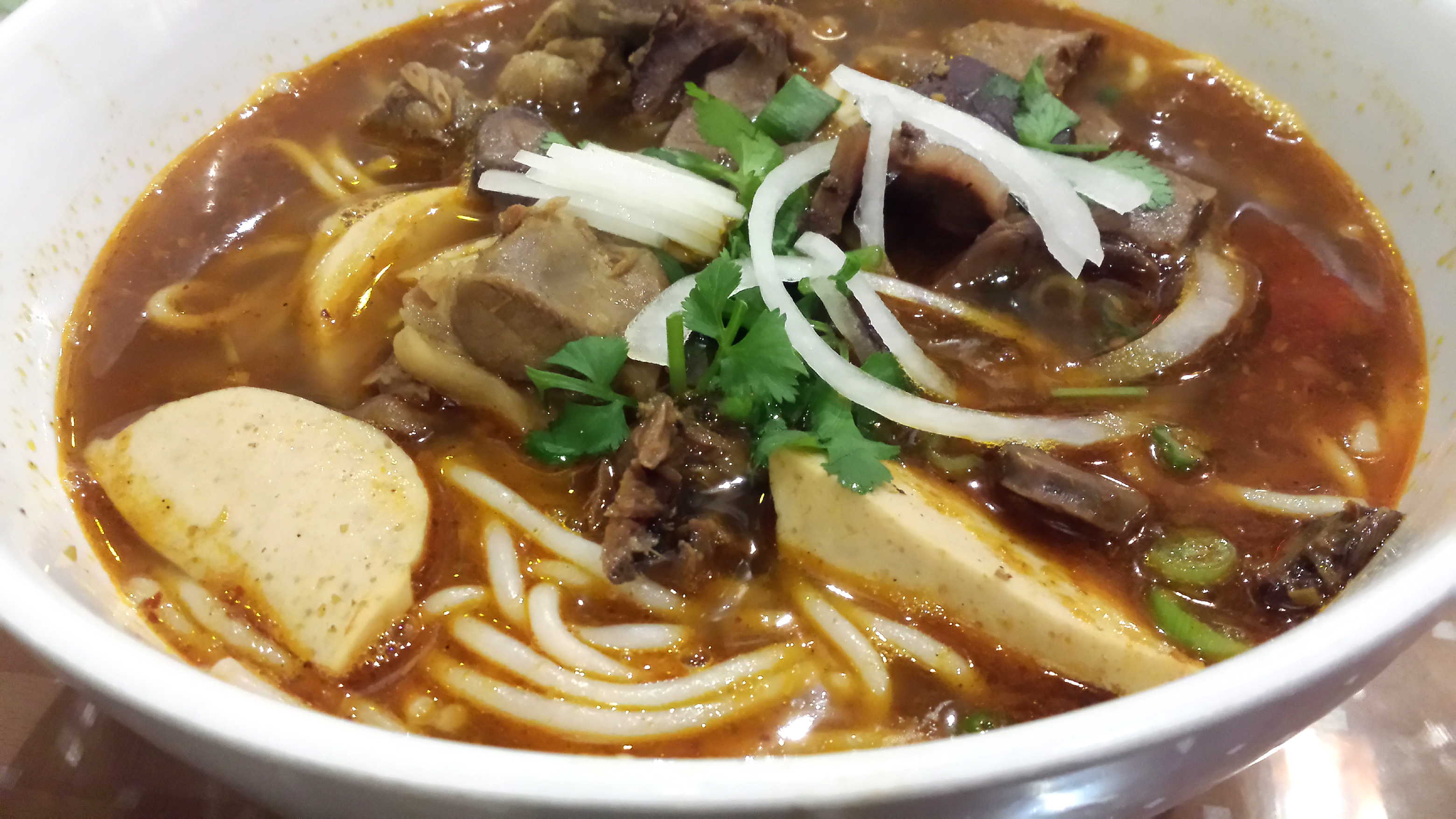
With ramen season kicking into high gear, I suppose it’s high time that I put out a guide to ramen for all of you cold, hungry fucks out there looking to get your soup on. This should serve as your singular, all-encompassing resource for all things slurp. This is more of an informational page, clearly, so if you’ve landed here looking for my ramen reviews, you should go to the Ramen-Ate-R page, where you can read about the tremendous shitload of ramen that I’ve eaten.
There are a bunch of things you need to keep in mind when thinking about ramen. Namely, you need to think about the thickness of the broth, how the broth is made, how it is seasoned, what kind of noodles are used, the toppings, and, finally (if you’re into food knowledge), where the ramen style was developed and the history behind the dish. So let’s get into it:
BROTH THICKNESS
This is classified as either assari (light) or kotteri (rich). Assari broths are generally thin or clear, as they are typically flavored with vegetables, fish or seaweed. If animal bones are used at all, they are usually just simmered lightly for a short amount of time.

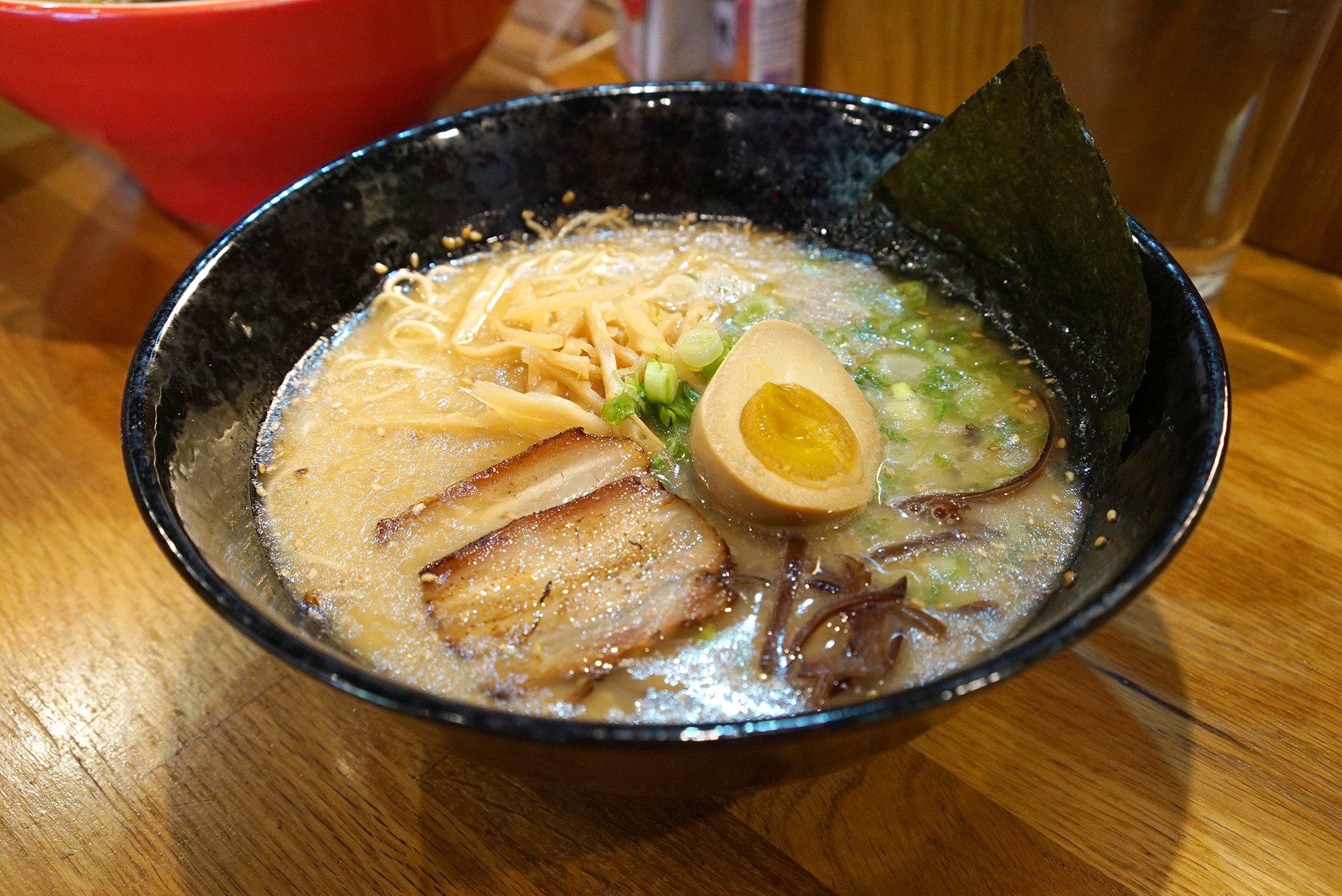
Kotteri, on the other hand, are thick and usually opaque, due to all the emulsified fats, proteins and minerals that are rendered from boiling animal bones for long periods of time. That makes them stocks, technically, not broths. Kotteri are also known as Paitan (from the Chinese). Paitan translates to white broth, which makes sense, given that they are usually cloudy in color and thick in texture.

SOUP BASE
Ramen soup bases are classified by the main ingredients that are boiled or simmered to make the soup stock (if bones are used) or broth (if no bones are used). As expected, a stock can be made from animal bones (chicken, beef, pork, fish). But lighter broths can be made with dried seafood or kelp/seaweed (like dashi – a broth made from dried, smoked bonito flakes and kelp), and sometimes even just straight up roasted veggies and mushrooms + water.

An example I will use to illustrate here is tonkotsu. “Ton” means pork, and “kotsu” means bones. Thus, the tonkotsu ramen base is a kotteri style thick stock made from pork bones, which would then need to be seasoned with a salty or savory component, which is covered in the next section.
SEASONING
Tare or kaeshi is the seasoning – the main savory element or source of salt – that is used to flavor the ramen. Ramen seasoning comes in three major varieties: Shoyu, Shio and Miso.
Shoyu: This, simply, is soy sauce. If you didn’t know, soy sauce is made from a paste of fermented and boiled soybeans, roasted grains and seasoned water.
Shio: Sea salt. Pretty straightforward. As you can imagine, sea salt as a seasoning is nicely suited for thinner, assari style broths.
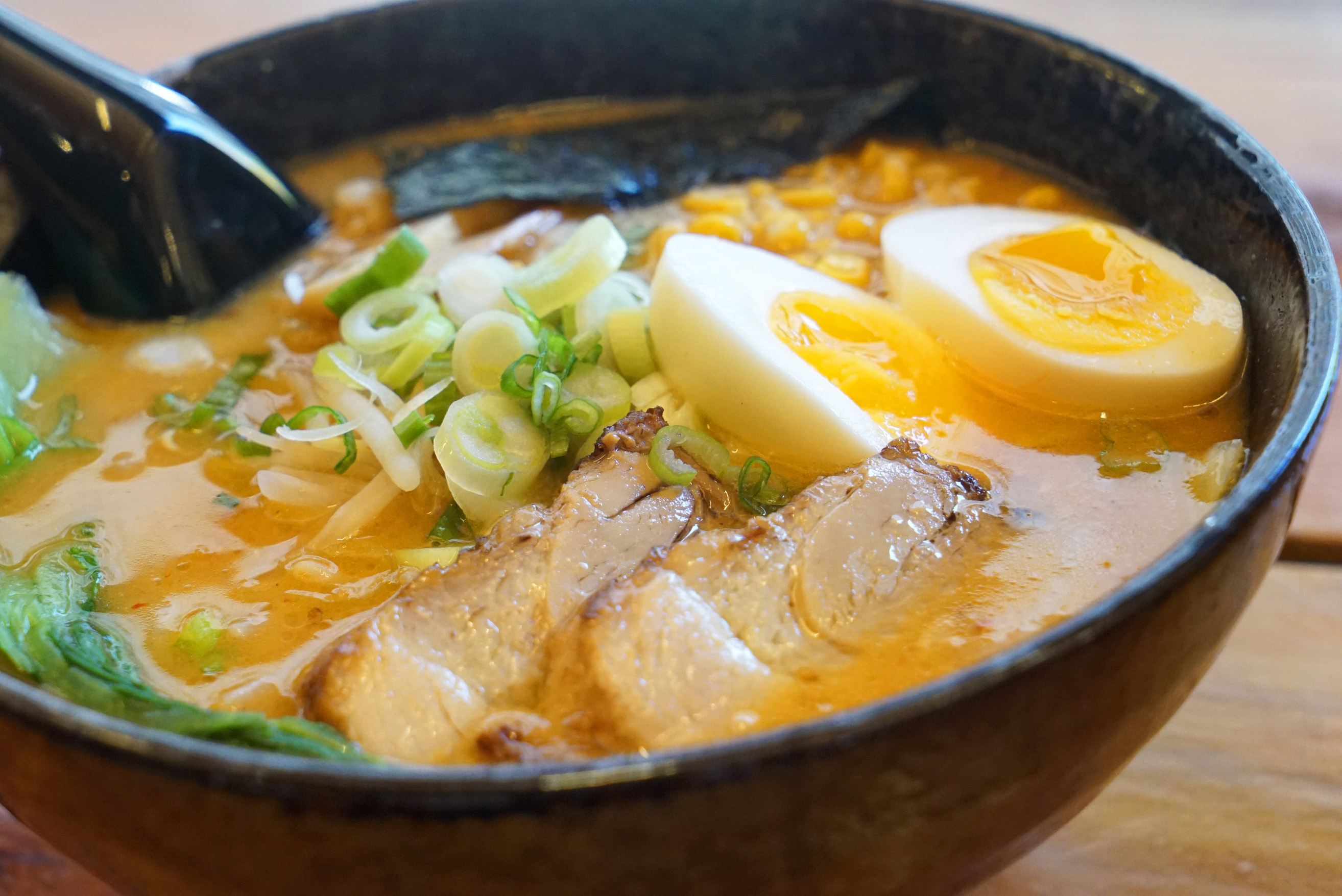
Miso: This is an earthy flavored, thick, fermented soybean paste. Seasoning with miso will almost always result in a thick, kotteri style broth, as you can see below:

NOODLES
Ramen noodles are made with wheat flour, water, salt and kansui, an alkaline water which gives the noodles their yellow color and characteristic bounce. In China, it’s more common to see ramen made with eggs instead of kansui.
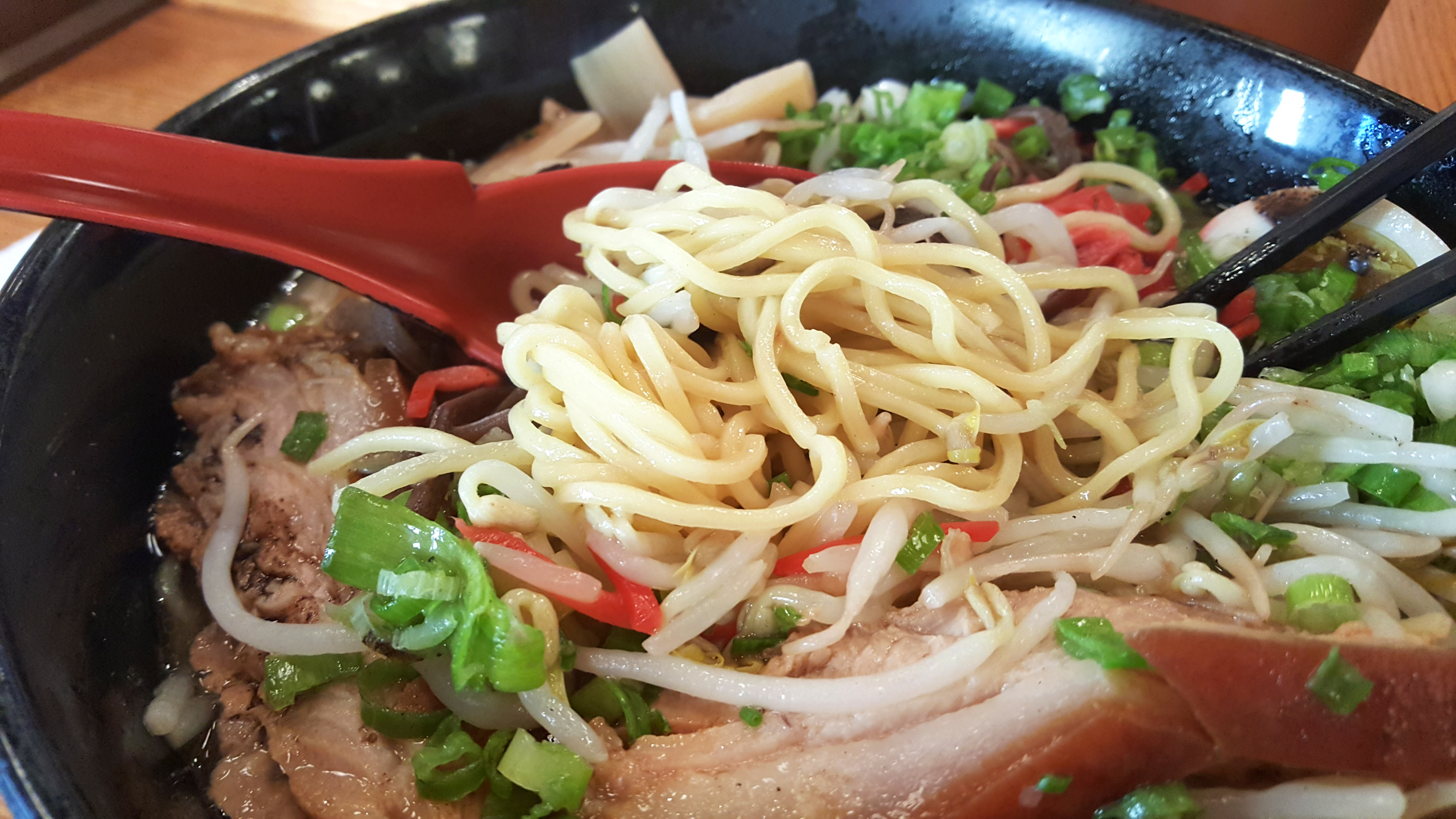

Depending on the soup they’re added to, ramen noodles can range from wavy to straight, thick to thin, flat, round or square. The type of noodle selected for a bowl of ramen is based on its broth-clinging characteristics, its bounciness and its texture. For that reason, one noodle style may be better suited for a particular soup base or broth thickness than another.
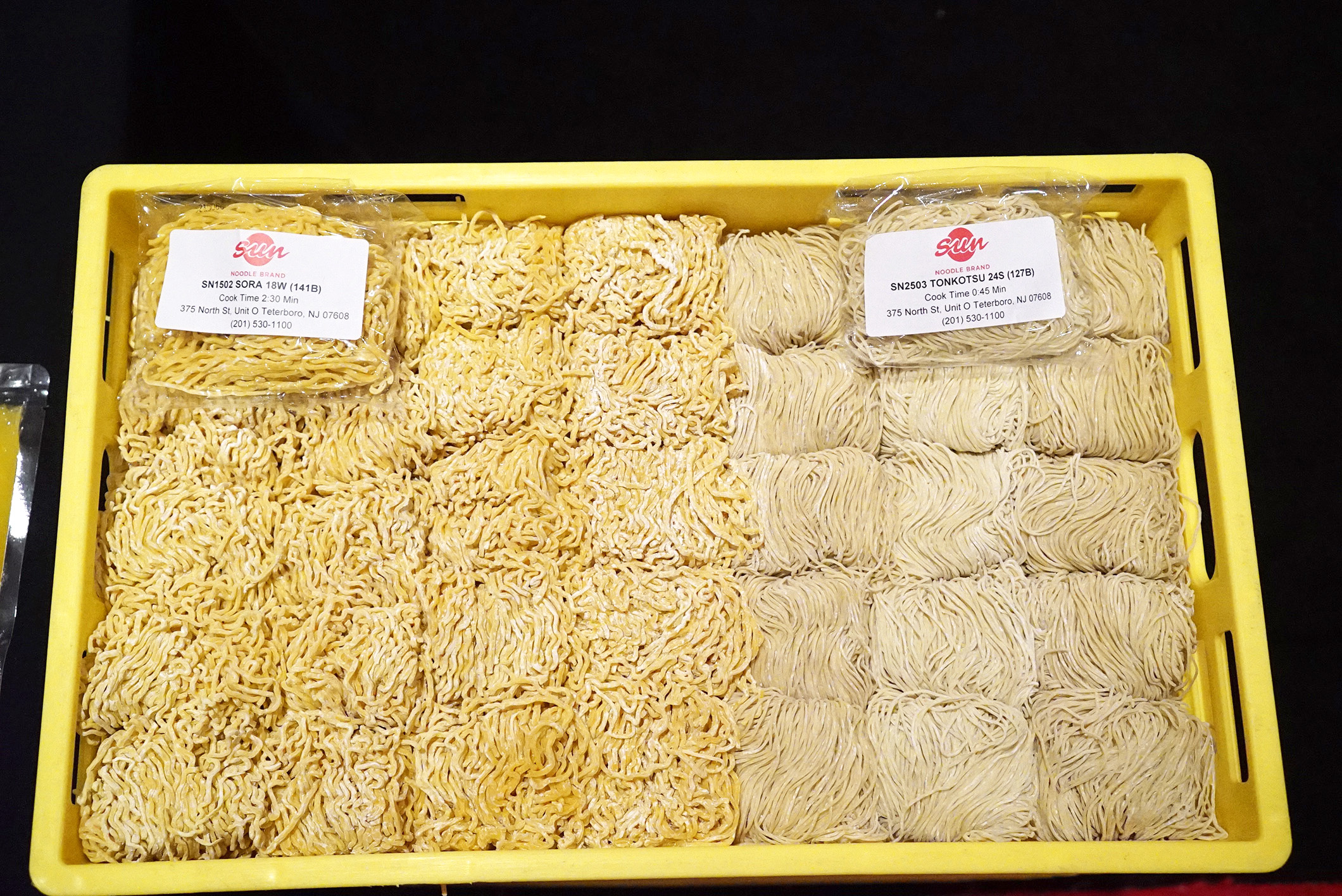

Depending on the noodles used, cook times will vary as well. In addition, their ability to last for a while, soaking in the soup broth, will vary. After a few minutes certain noodles will lose their spring and bounce, and the texture will change.

Just an FYI here: if you need more noodles while you are eating, yell out kaedama!
TOPPINGS
We have a bunch of categories to discuss here. Let’s start with the most important one: meat.

Obviously if a ramen base is made with animal bones, it only makes sense to use the same animal meat as a topping for the soup. Tonkotsu should have copious amounts of kakuni (pork belly), or chashu (rolled pork loin or belly that is cooked slowly in a sweet soy and mirin sauce, stew-style, then sliced and sometimes charred or grilled afterward for texture). Clearly, chicken is a good topper for your chicken-based ramen. But some chefs get creative. For example I’ve had beef ramen that was topped with crispy beef intestines. I’ve even had chicken broth that was topped not only with chicken but with ground pork as well. Mixing is not a bad thing and it is quite common, as you’ll learn below.
In addition to meat, ramen broths also contain aromatics, such as garlic (fresh, charred, fried or fermented), onions (charred, pickled or raw), ginger (either pickled – beni shoga – or fresh), leeks (fresh or charred), scallions (usually fresh, typically sliced or shredded) and mushrooms (both dried and fresh, and a ton of different types). These can also be incorporated into the creation of the soup base at the start, not just as toppings that are added at the time of serving.

Other common toppings include seasoned soft boiled or hard boiled eggs, sliced fish cakes (naruto), bamboo shoots, corn, cabbage, seaweed, bean sprouts, spice pastes, butter and various oils, such as chili oil, onion oil, pepper oil, garlic oil or sesame oil (and certainly sesame seeds, too, for that matter).

On many occasions, the toppings you see will depend on the region in Japan from which the ramen hails.
REGIONAL STYLES
Japanese ramen varies greatly by region. Some areas focus on thinner fish- and seaweed-based broths, while others tend to be hearty and thick animal bone soups. I’ve highlighted some of the regional styles below, alphabetically:
Akayu: A sweet and mild ramen soup is topped with a spicy dollup of miso mixed with chili and garlic. Chewy, thick, wavy noodles grace this style, and it is usually served with powdered seaweed as well.
Asahikawa: Asahikawa is Hokkaido’s second-largest city, and is located at the base of the mountains in the middle of the island. Its ramen is a mix of chicken, pork and seafood broth, with a shoyu base. The soup is topped with a layer of melted pork fat to seal in the soup’s heat in the colder months, as well as pork meat, bamboo shoots and scallions.
Hakata: Also known as Nagahama ramen, this style comes from Fukuoka, a prefecture in Japan’s southern island of Kyushu, which is famous for its pork dishes. This is my favorite of ramen styles, because it is a thick, fatty, pork bone broth with thin, al-dente noodles. Toppings usually include sesame seeds, pink pickled ginger and fried garlic.
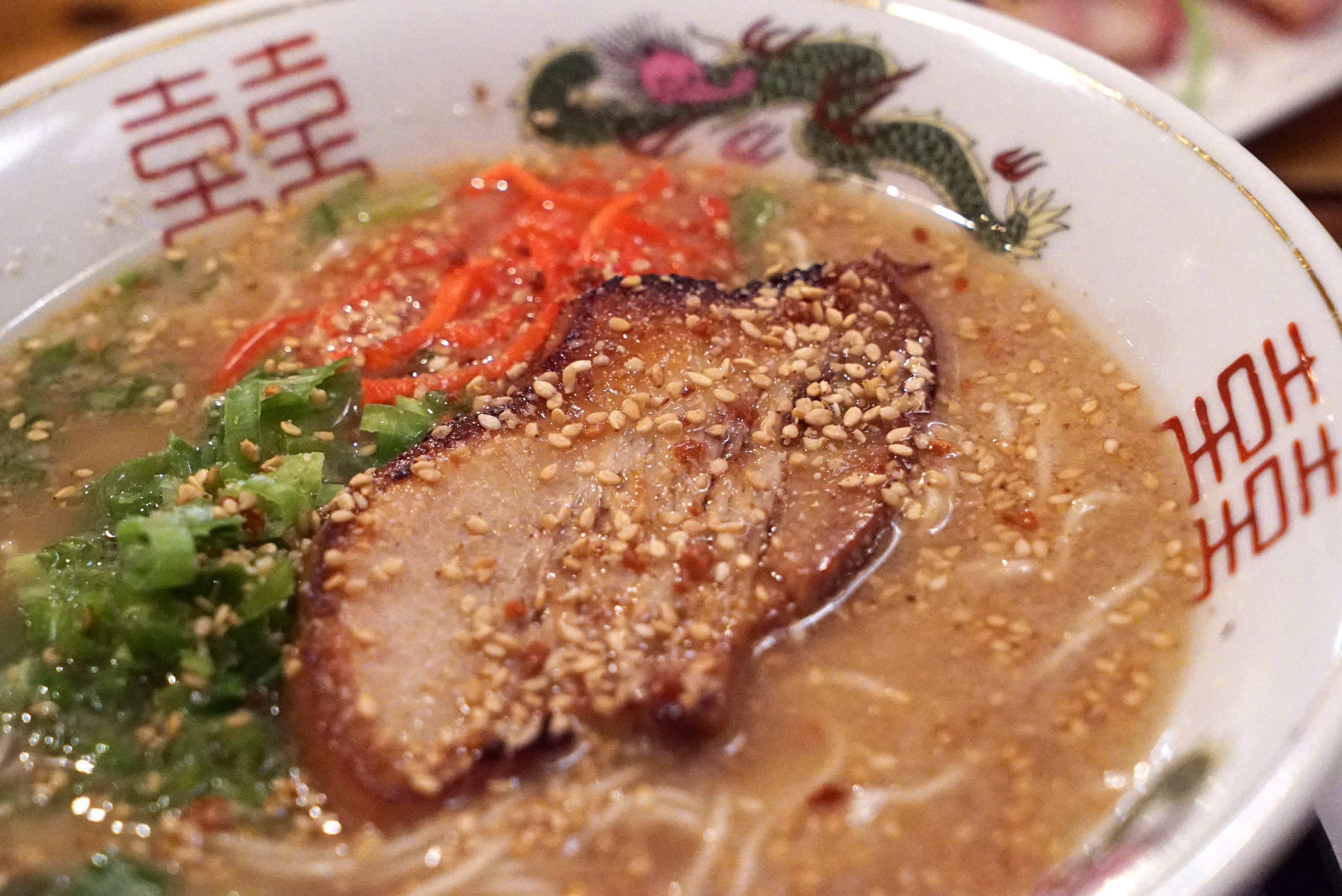

Hakodate: Ramen arrived in Hakodate from China. The soup is thin and light, and the shio-seasoned broth had a mild pork and chicken base. Noodles are usually soft, with toppings like roast pork, bamboo shoots, scallions, nori, fish cakes and spinach.
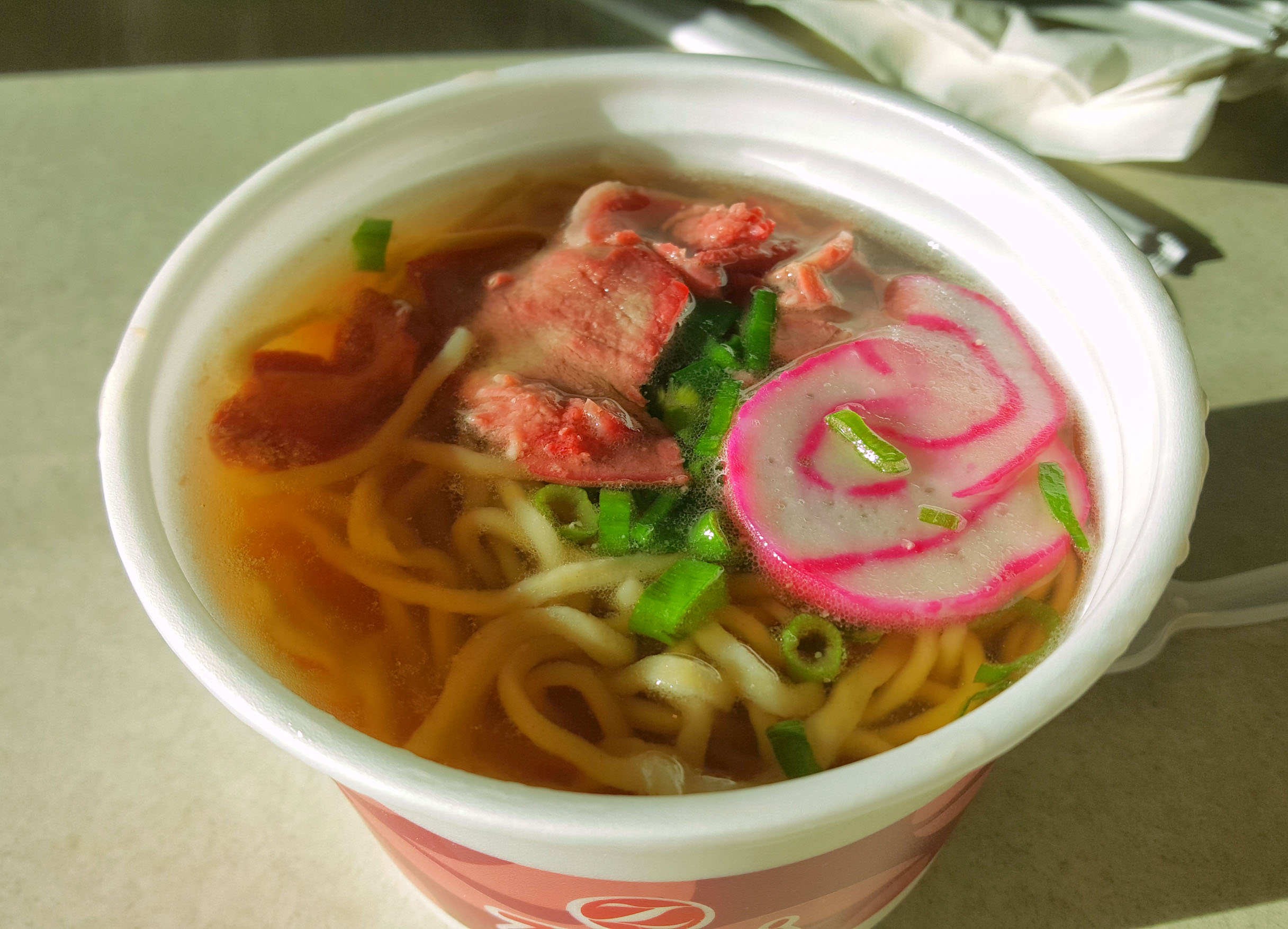

Kagoshima: Kagoshima is known for its Berkshire pork-like black pigs, yet the ramen is a mild mix of both veggies and chicken, combined with the black pork bone stock. The broth then gets finished off with burnt onions and seasoned with soy sauce. The noodles are soft, and toppings consist of pork meat (obviously), scallions, wood ear mushrooms (kikurage) and bean sprouts.
Kitakata: Kitakata is famous for a clean, light soy-based breakfast soup. In the bowl there’s usually a serving of chewy, wide, flat and curly hand-cut noodles with pork, scallions and bamboo shoots.
Kumamoto: When tonkotsu ramen arrived in Kumamoto prefecture from Kurume, the locals started cutting it with chicken broth. It’s also served with straight noodles, though they’re softer and thicker than the Kurume style. Most bowls have pickled mustard greens, sliced wood-ear mushrooms, bean sprouts, and cabbage on top, but the unique thing about Kumamoto ramen is the use of garlic. You’ll see fried garlic chips and mayu, the black liquid made from garlic that’s been burned in sesame oil. That shit is delicious.

Kurume: This town on the southern island of Kyushu is the birthplace of tonkotsu. Melted bone marrow, fried lard, sesame seeds, pickled ginger and garlic give Kurume ramen a unique and pungent style. Toppings include pork meat, scallions, nori, and spicy mustard greens, in addition to those just mentioned above.
Kyoto: Kyoto’s home to two distinct types of ramen: a thinner assari shoyu ramen, and a thick kotteri chicken soup. The thin version is a blend of pork and chicken broth, with a dark soy base. The thick version is a rich porridge-like chicken soup, topped with garlic, spicy bean paste, chives and odoriferous local onions called kujnoegi. Both are seasoned with shoyu, but the toppings vary for each.
Nagoya “Taiwan” Ramen: “Taiwan Ramen” is Nagoya’s reimagined version of Taiwanese danzimian, which has lots of ground pork, Chinese chives, hot peppers, green onions and garlic. This shit is for people who like spicy soup.
Onomichi: Take a bit of pork, a heap of chicken, some local seafood and a big mess of lard and you’ve got Onomichi ramen. The soup has a shoyu base and is served with chewy, homemade, wavy, flat noodles. It’s usually topped with roast pork, bamboo shoots, scallions and pork fat.
Sapporo: Sapporo-style ramen hails from Japan’s northernmost province, Hokkaido, which is the birthplace of miso ramen. Sapporo miso ramen generally has thick, strong noodles and is commonly topped with bean sprouts, sweet corn, cabbage and ground pork. Soft boiled eggs and thick slices of chashu pork are also common, as well as pats of butter.
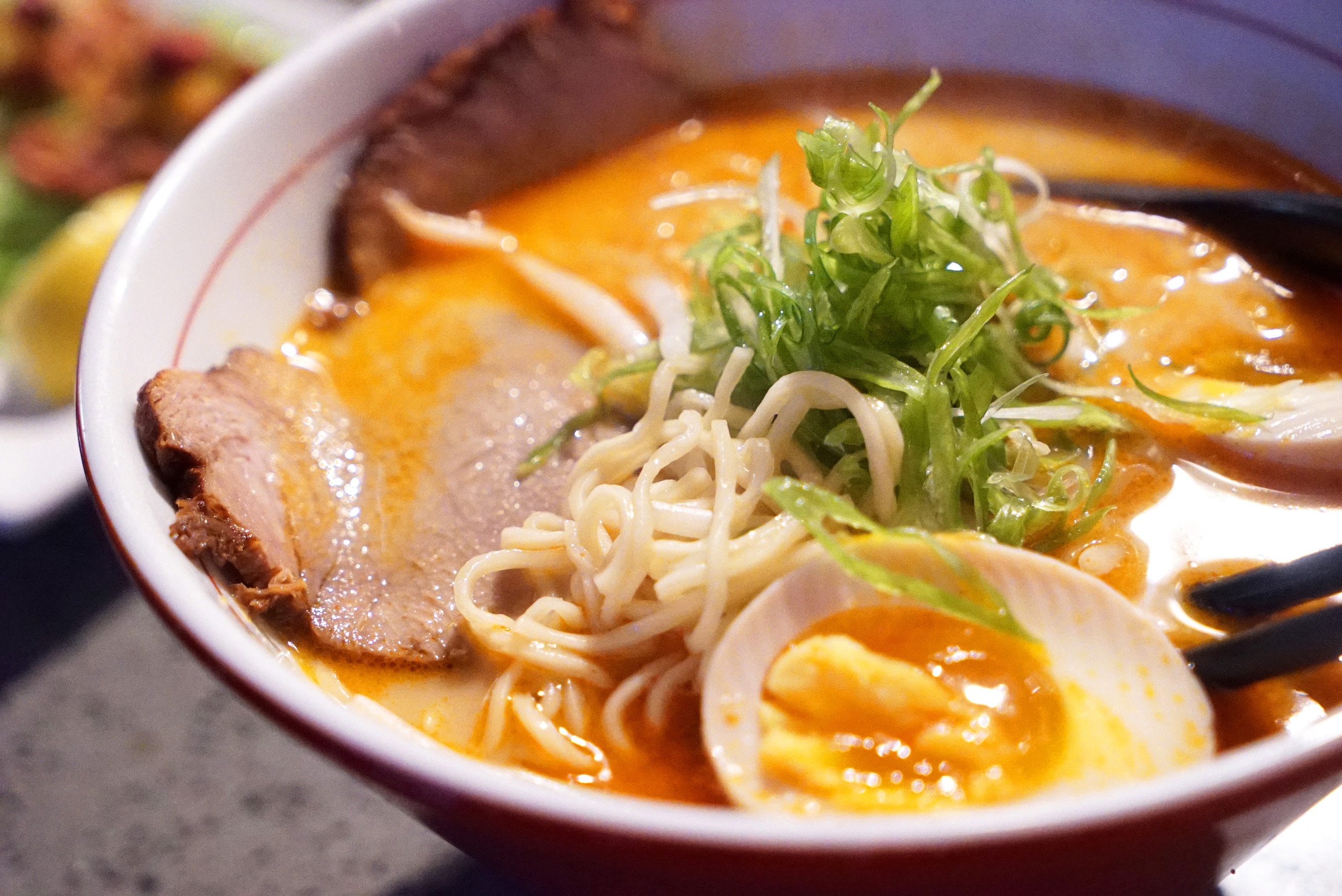

Shirakawa: This town developed a refined ramen typified by light, simple soup and hand pulled noodles. It features a shoyu broth, but local mineral water makes for springy noodles with a good chew. Toppings include roast pork, bamboo shoots, fish cake, scallions, seaweed, spinach and even wontons.
Tokushima: Shikoku is the smallest of Japan’s four main islands, and udon is the preferred noodle. But Tokushima prefecture has an aged, extra strong shoyu soup that originated with tonkotsu stocks made from leftover pork bones from nearby ham factories. This is similar to Wakayama ramen. Ramen shops here will add a few strips of thinly sliced pork belly and break a raw egg on top. Tokushima ramen is sometimes divided into “yellow,” “black,” and “white” styles (how racist) of varying strengths. Other toppings for this ramen consist of scallions, bamboo shoots and bean sprouts.
Tokyo: This ramen is usually made with pork and chicken broth and typically features slightly curly, somewhat wide noodles. Very often in Toyko you’ll find broths that are flavored with dashi (broth made from aged bonito flakes and sea kelp). This style of ramen is generally seasoned with shoyu and has a medium-thickness. It’s similar to Yokohama ramen, though that tends to be heavier and meatier than the dashi broths of Tokyo ramen.
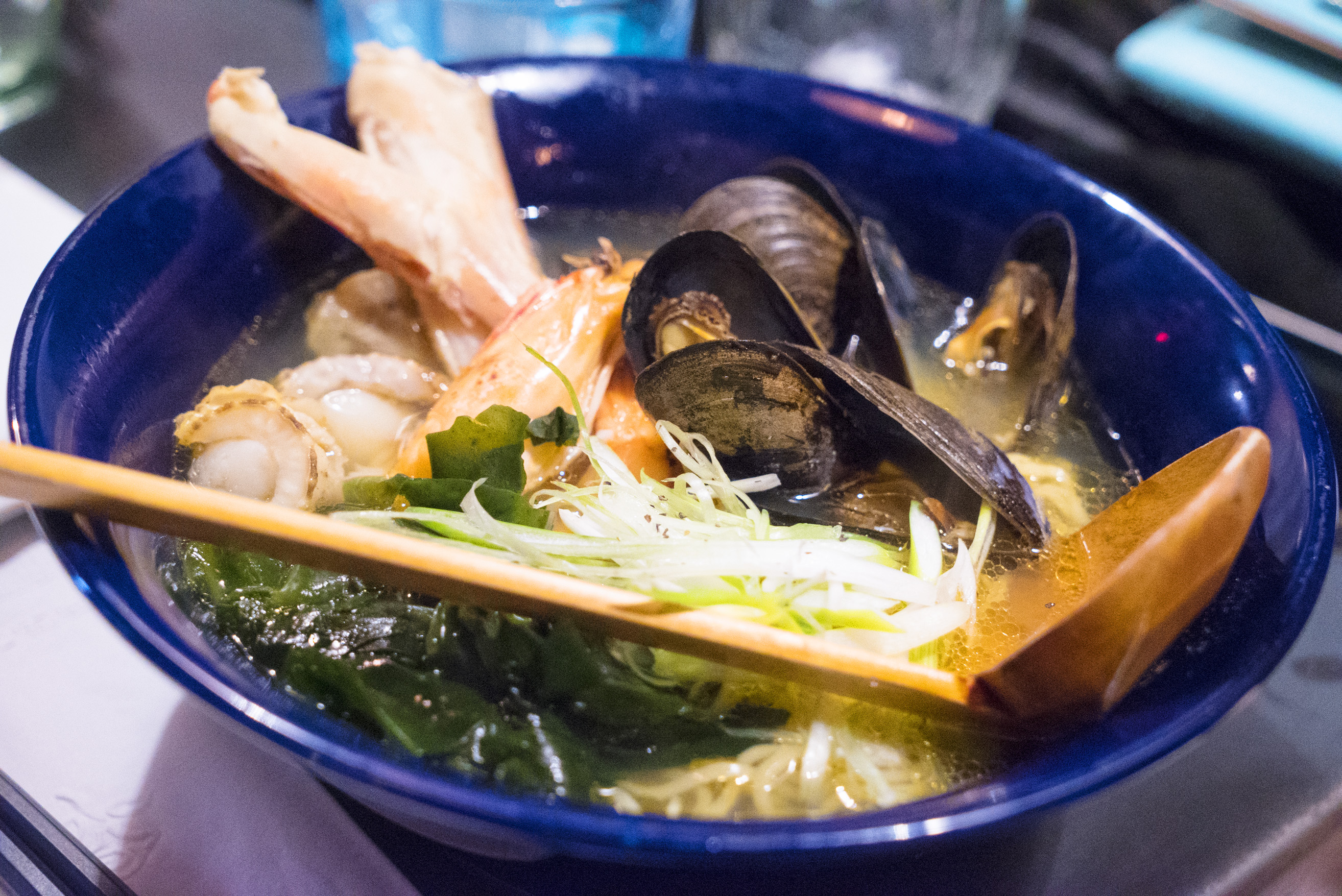

Tsubame-Sanjo: The cities of Tsubame and Sanjo are in a freezing cold area, and the ramen from this spot is bizarre and unhealthy. The hearty stock is made of chicken, sardines and pork bones, and the bowls are blasted with tons of pork fat (common in soups from the colder climates). There’s thick, flat noodles in this shoyu-based soup, and toppings include pork meat, bamboo shoots and lots of chopped white onions.
Wakayama: This is the median between thick, rich tonkotsu, and thin, clear broth. Wakayama ramen has a strong shoyu tare seasoning with a long-simmered tonkotsu base. The noodles resemble the thin, firm and long threads of Hakata style ramen, but you also get fish cakes like those in Tokyo style ramen. These soups are also topped with the seemingly ever-present and most common of toppings: roast pork, scallions and bamboo shoots.
Yokohama Ie-Kei: Yokohama is known for ie-kei ramen, a viscous, salty, and fatty tonkotsu shoyu style of ramen. When ordering, diners can designate how firm they want their noodles, the amount of fat they like on top, and the saltiness or strength of the soup. This is my kind of ramen – catering specifically to each unique diner. The toppings for this style of ramen usually include sheets of nori (seaweed paper), spinach, garlic, spicy bean paste and ginger.
RAMEN-LIKE DISHES
Although these dishes are not quite ramen, they’ll still be able to satisfy the most intense need for a ramen fix.
Abura Soba: The name of this soupless noodle dish translates to “oil noodles.” It consists of cooked ramen noodles dressed with flavored oil and tare (usually shoyu). It often comes topped with an egg, and diners are meant to stir everything together in the bowl to form a creamy, fatty, thickened sauce. One can also add vinegar, chili oil and other shit before slurping. Hot peppers, mayonnaise, fried noodles, chopped garlic and pork fat are also crowd favorites to add in.
Chanpon: This originated in Nagasaki and is made by boiling thick noodles directly in a thick pork and seafood soup. It’s viscous, and eats more like stew than ramen.
Hiyashi Chuka: This literally means “cold Chinese.” As such it’s a dish made with cold ramen noodles and various toppings like fried egg, ham, carrot, cucumber and chicken. It is usually dressed in a light soy-vinegar sauce. I’ve even seen fish sauce used in some versions around NYC.
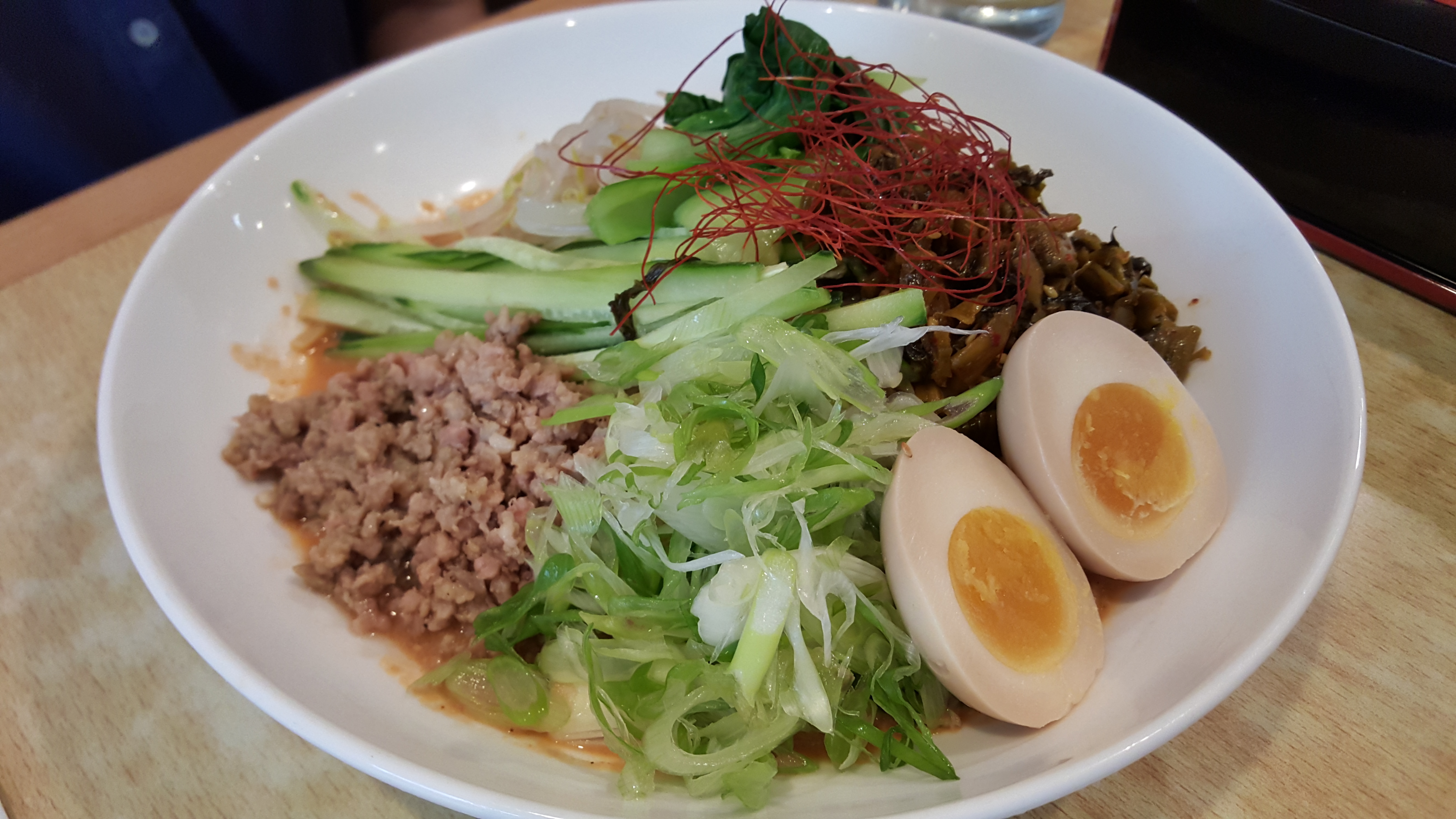

Mazemen: This is a hearty “dry” ramen, characterized by thick noodles and weird toppings like cheese. Similar to Abura Soba, this is essentially cooked noodles with a small amount of strongly flavored sauce on the side for dipping. Toppings and sauces can vary a great deal, and are often experimental in nature.
Tantan-Men: This is an off-shoot of Chinese dandan noodles. Based on a pork broth, it comes with a scoop of heavily spiced ground pork and is generally served with bok choy and/or spinach.
Tsukemen: This, like Mazemen, is also a “dipping” ramen. Cold, undressed (nekkit) noodles are served alongside a hot, concentrated ramen broth. You dip the noodles into a bowl of broth as you eat, grabbing the toppings whenever you choose to.
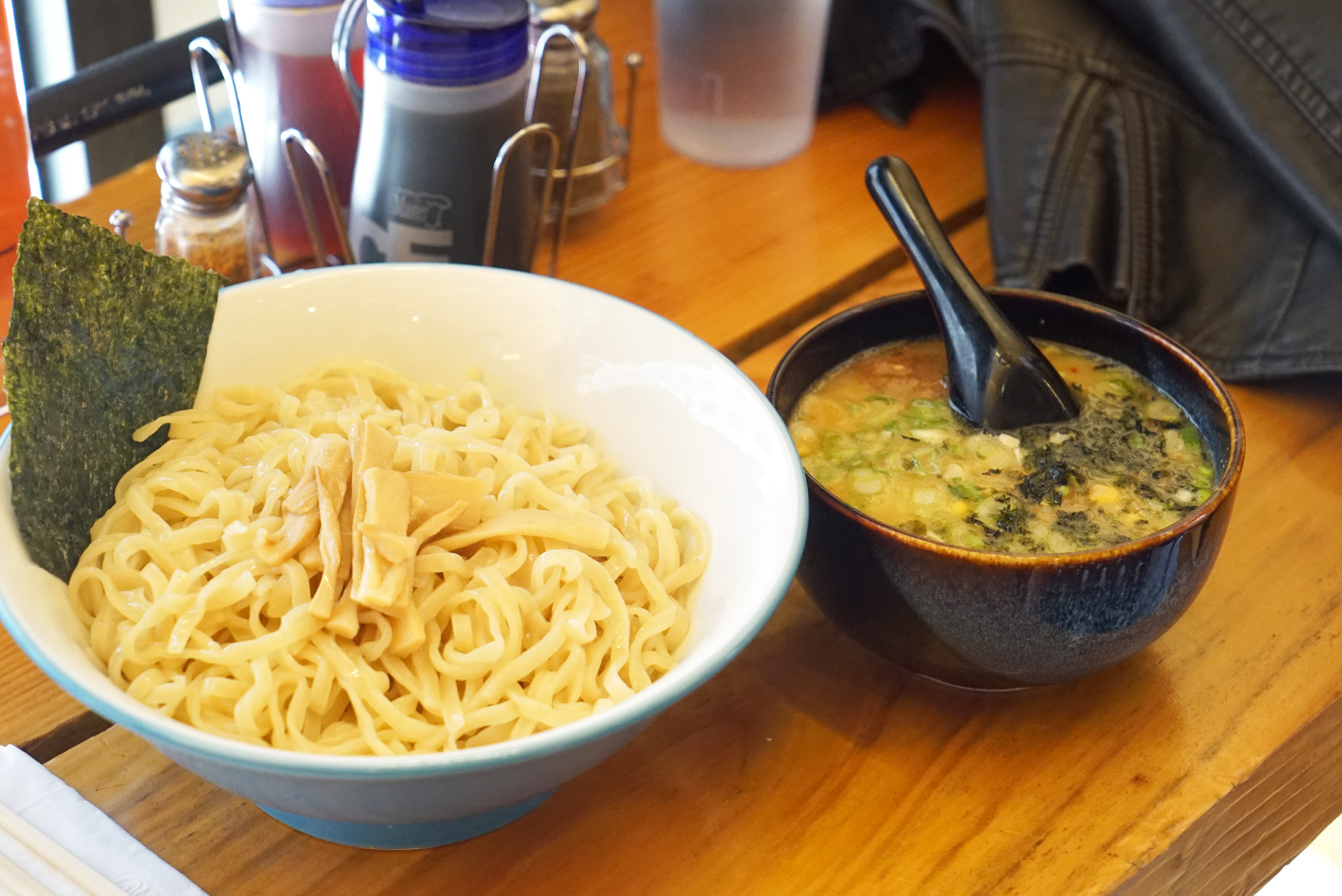

Yakisoba: This is the Japanese version of Chinese fried noodles. It’s made with egg noodles that get stir-fried with veggies and occasionally meat or seafood. This shit then gets hit with a Worcestershire style anchovy and vegetable sauce. It’s often topped with shaved bonito flakes and pickled ginger (beni shoga).
FUSION RAMEN
All around NYC we are seeing various kinds of fusion ramen items being offered, which makes a lot of sense given that the history of ramen in Japan involves a lot of Japanese-Chinese fusion.
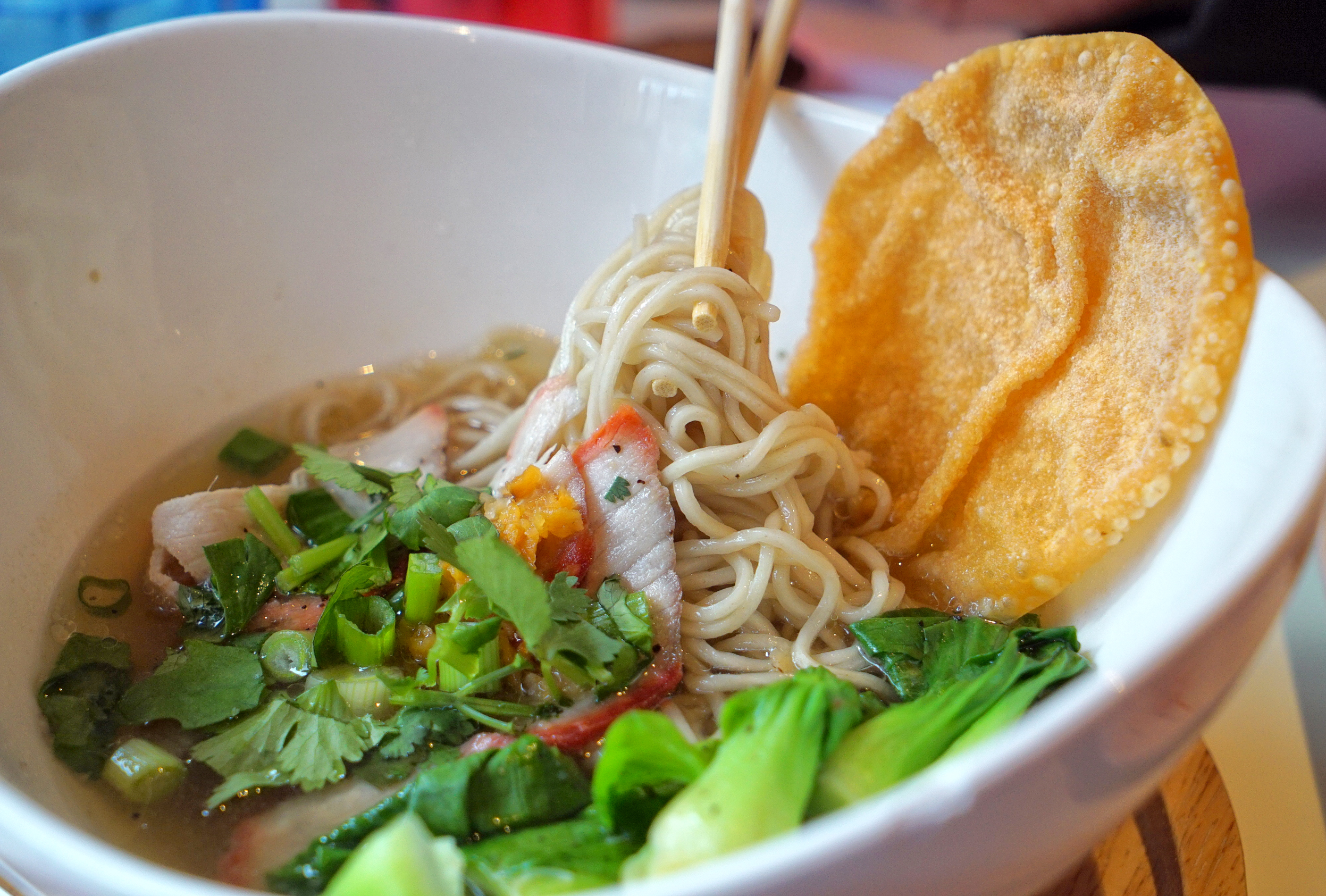

However some of the more wild examples I’ve seen in NYC include:
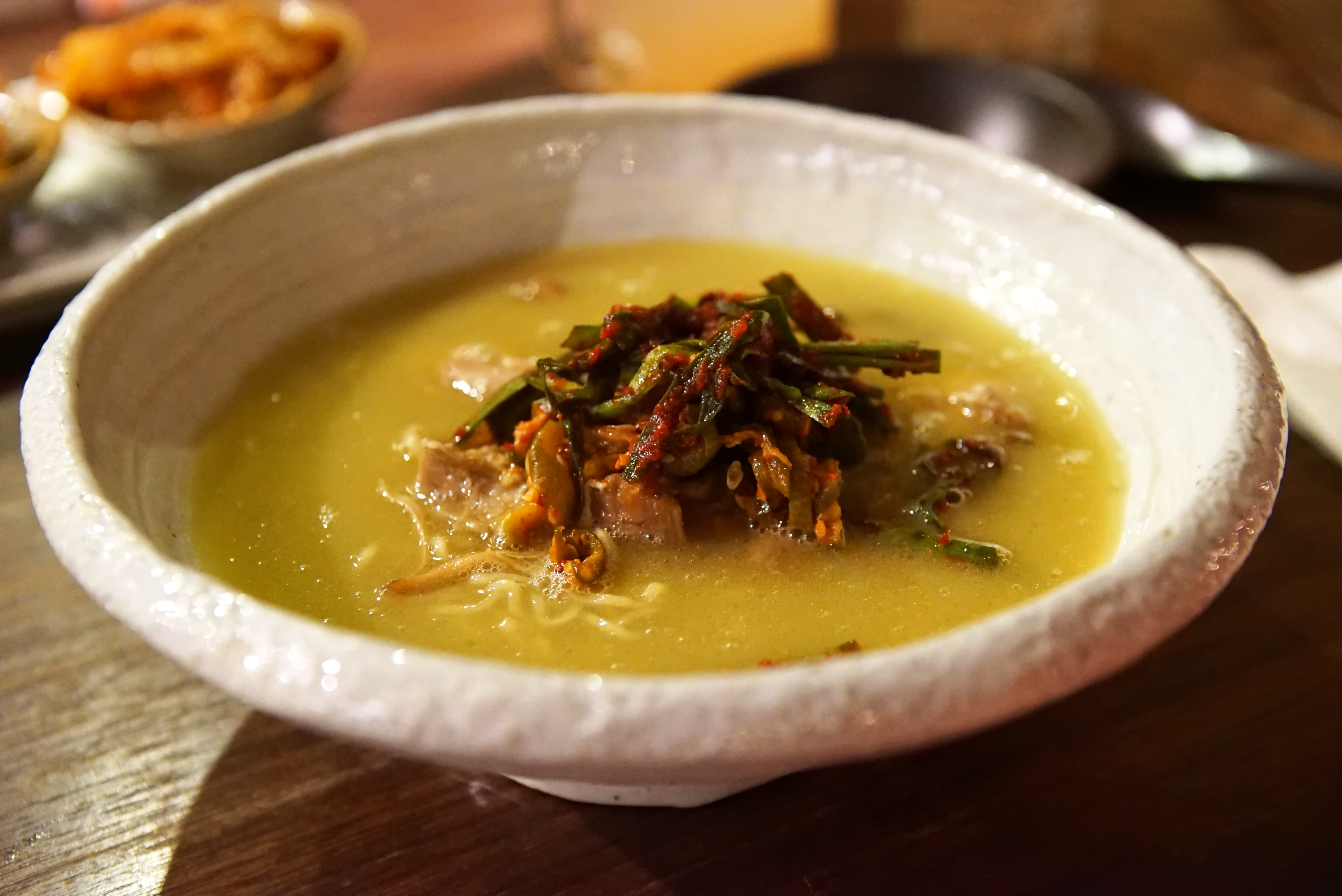
Korean-inspired kimchi ramen (Mokbar):

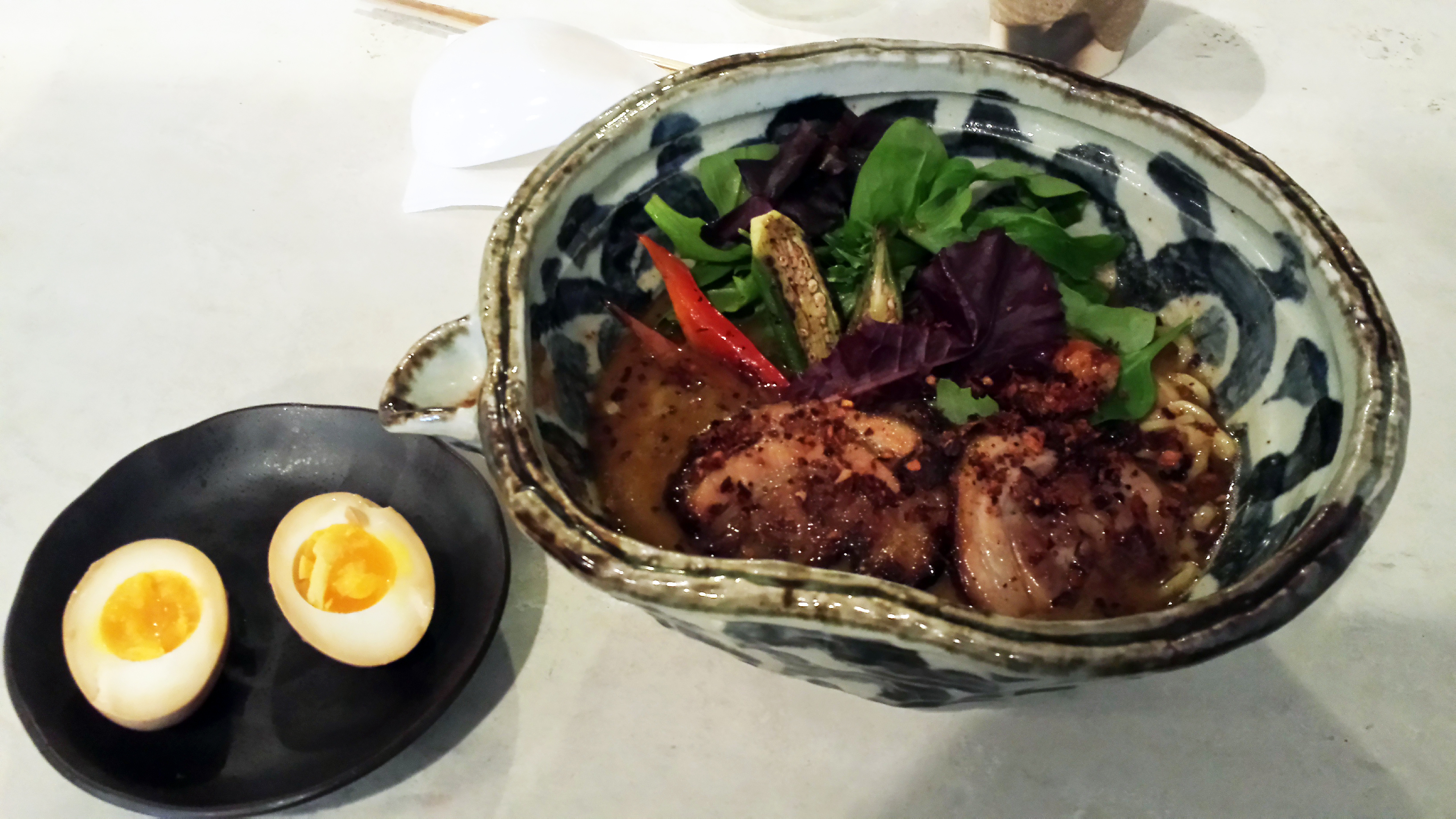
Thai green curry ramen (Bassanova):

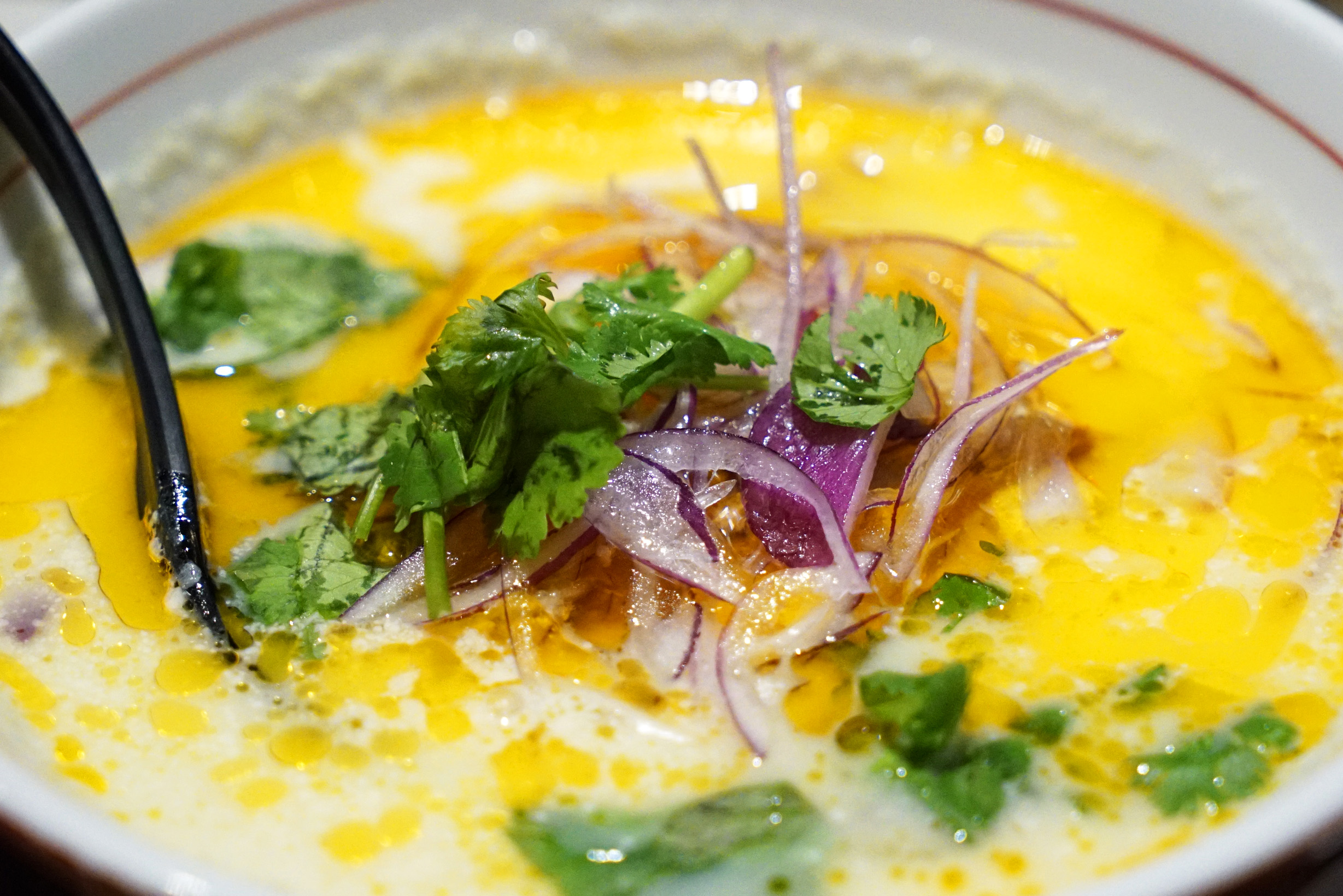
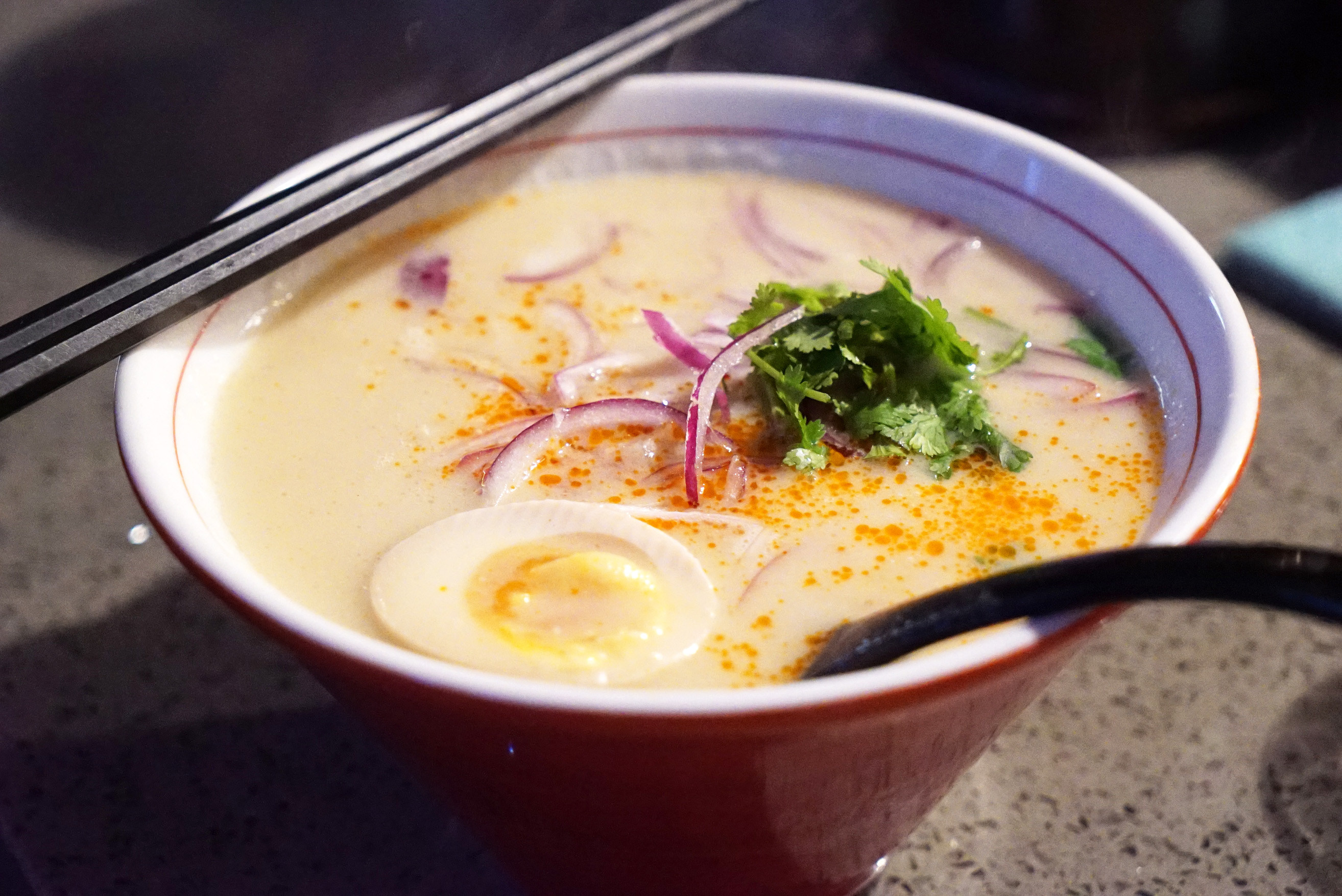
Flavors common to Burmese cuisine that feature coconut milk in the broth base (Tabata):

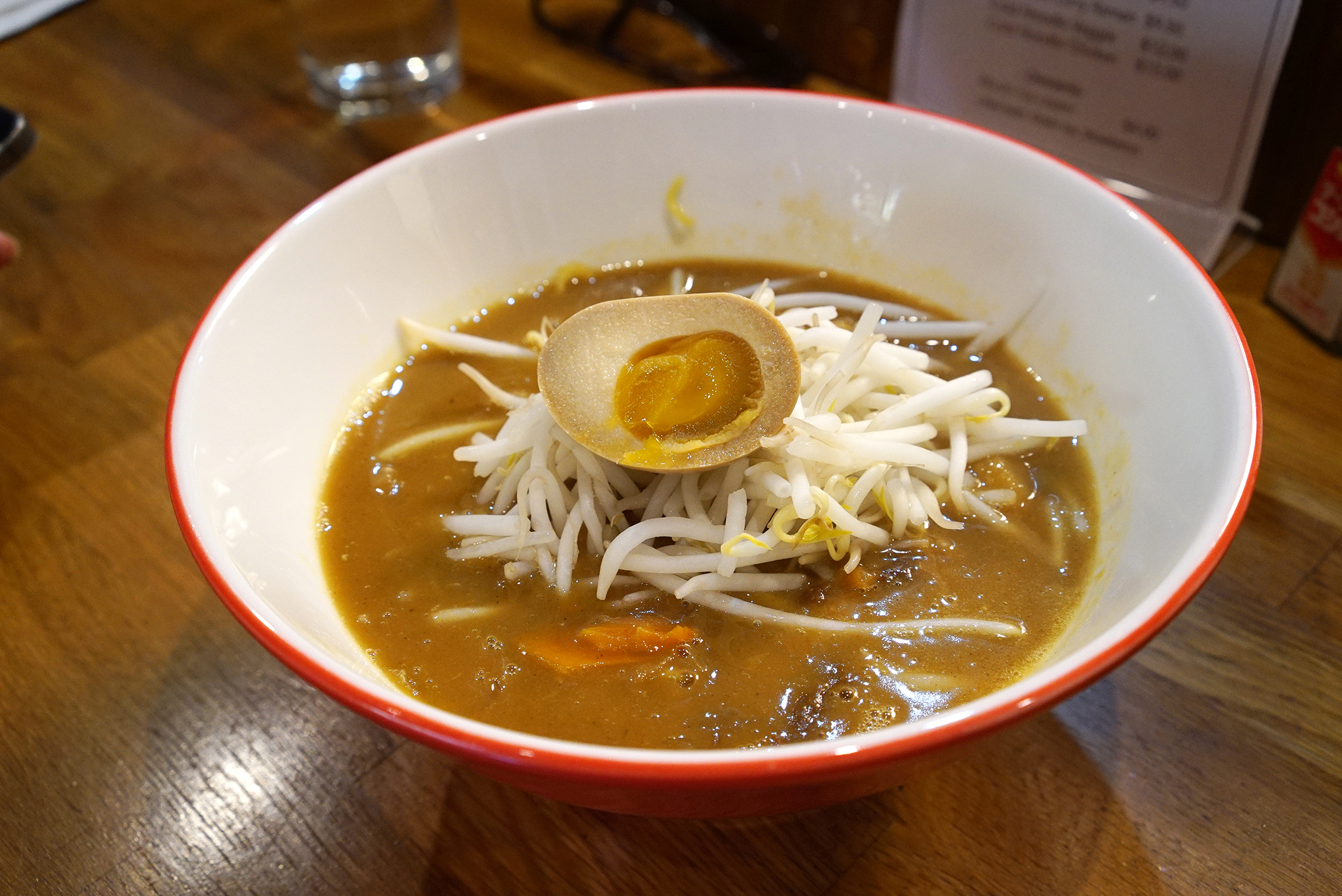
Indian-inspired massaman curry ramen, even complete with potatoes and carrots and (Yasha):

Italian spaghetti ramen, with pepper oil, arugula and crispy porchetta (Maialino):

Thanksgiving turkey ramen, with gravy, mushrooms, stuffing and cranberries, of course (Talde):
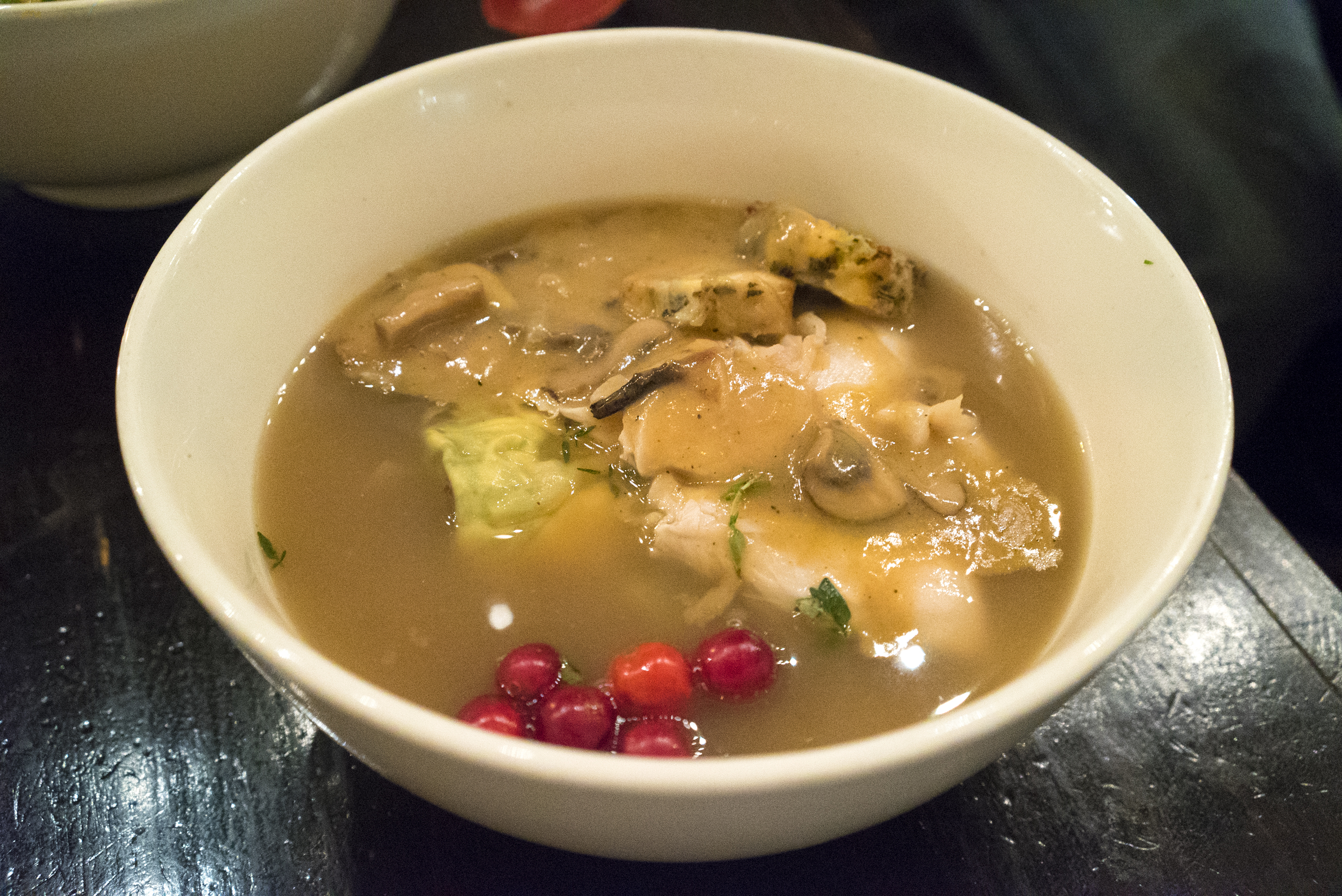

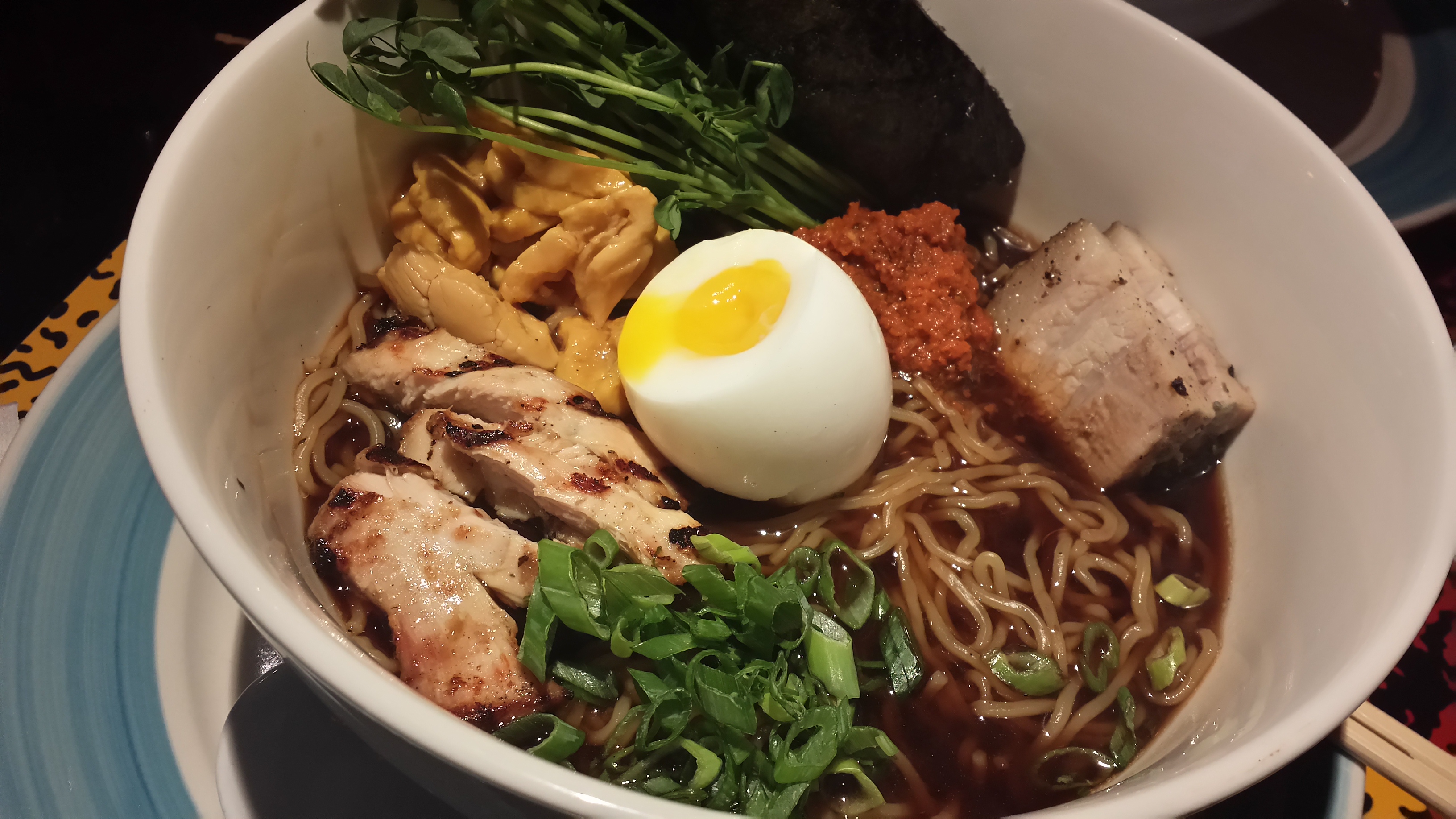
And Jamaican jerk chicken ramen (Miss Lily’s 9A):

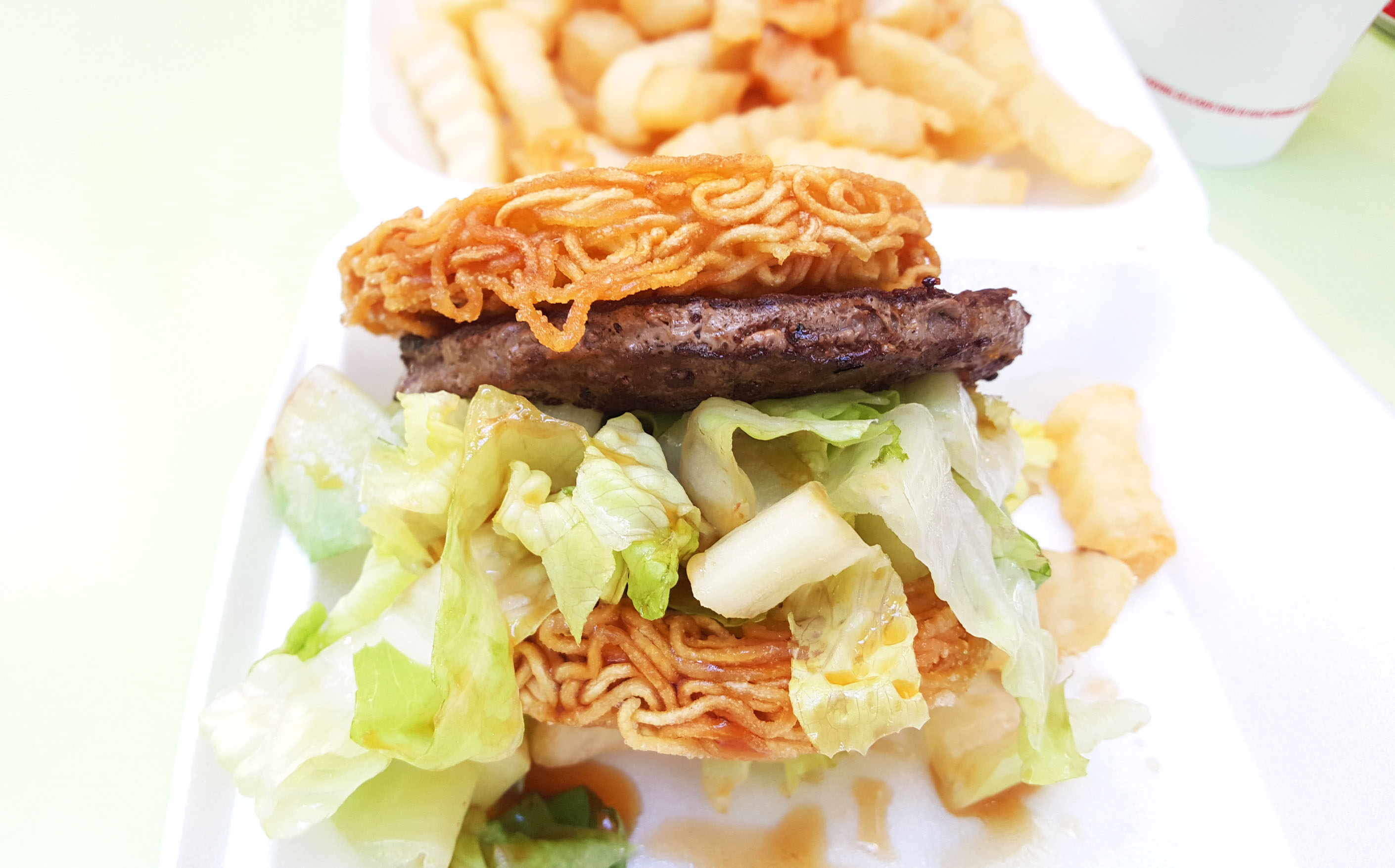
There are even ramen burgers (L&L Drive Inn, among others)…

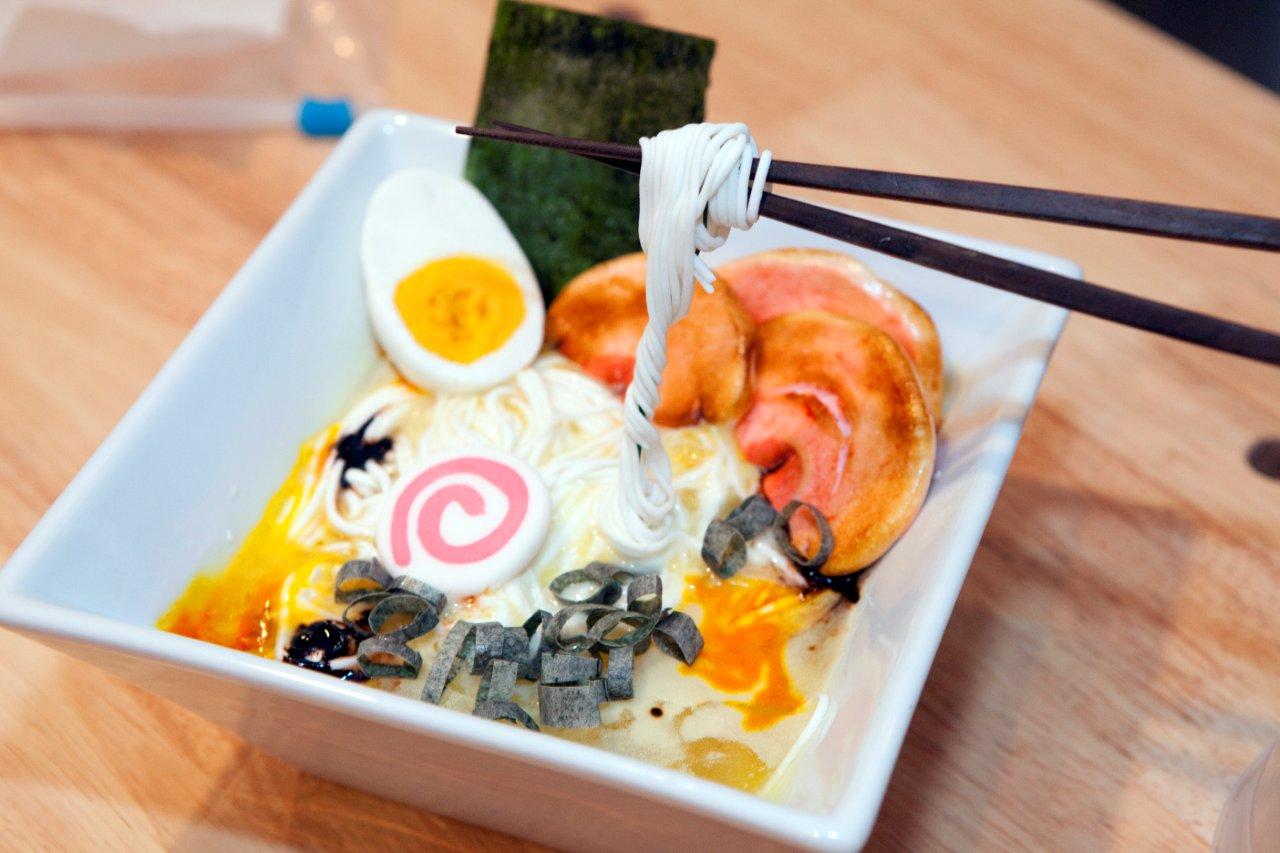
…and now ramen cake (courtesy of my wife, The Cake Dealer).

So that about does it here. If ramen isn’t your thing, but soup most definitely IS your thing, as a general matter, then there’s always pho, bun bo hue and laksa out there to soothe your hot soup needs in the cold winter weather that’s about to strike.