My wife found this awesome series of “Meat Your Beef” / “Farm to Fork” tours that the New York Beef Council (@newyorkbeefcouncil) hosts at various local farms in the area. The national outfit is known by the popular moniker: “Beef; It’s What’s for Dinner,” with the accompanying website as well. I sometimes link to their butchery videos here, actually. It is an extremely helpful organization!
So the closest farm tour to NYC that they set up was in Millbrook, at a place called Walbridge Farm (@walbridgefarmmarket). Millbrook is a rural community in the heart of the Hudson Valley, just about two hours north of NYC. Walbridge Farm is an Angus beef farm.
The best part about this, aside from the wealth of knowledge we come away with, is the fact that these tours are completely FREE and we were even treated to a steak lunch. I was sold on “free beef farm tour,” but “free steak” was icing on the cake. We immediately RSVP’d and rented a car for the day, and Jeff from Foodmento and his wife Victoria came with us.
So we pulled off the Taconic to a nice country road that was dotted with awesome creepy and abandoned structures. I have a soft spot for these in my photography, so I snapped a bunch of shots. We were about 30 minutes early for the tour anyway.
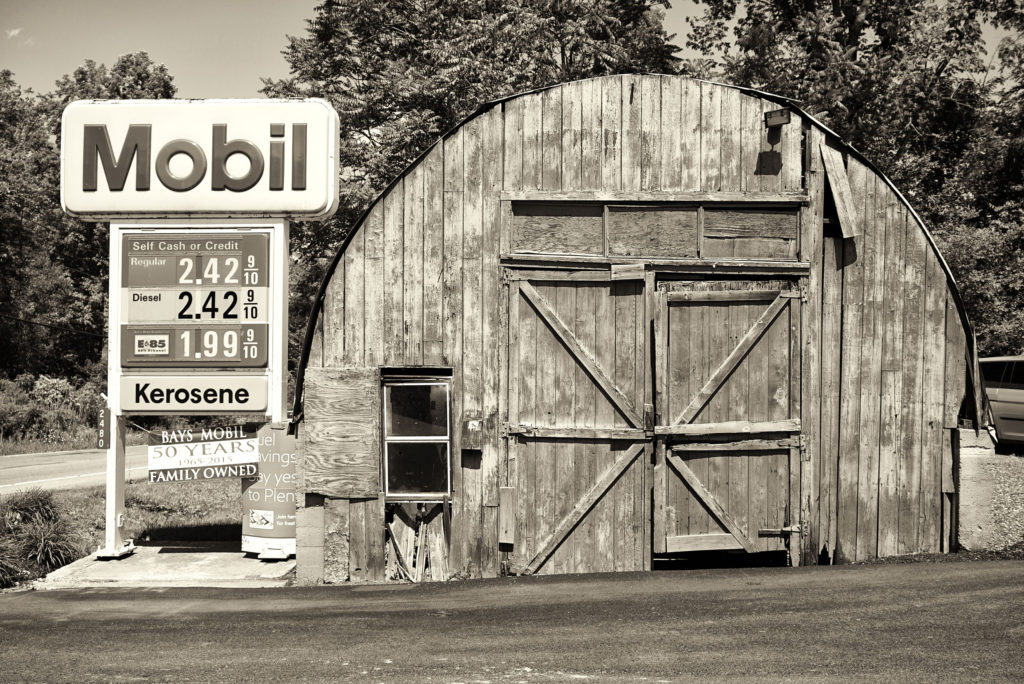
First was this banged up looking shed at a Mobil station:

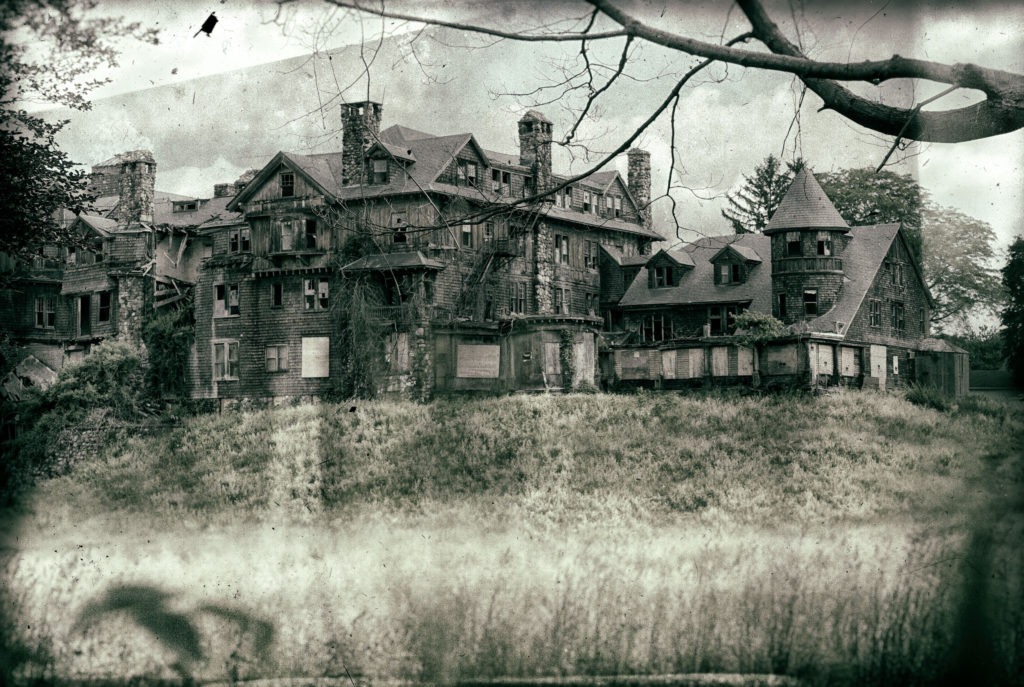
Then we spotted this monster of a mansion along the north side of the road. Upon further examination, we learned that it was the Halcyon House. Once a luxury hotel, it was later transformed into the Bennett School for Girls, a boarding school and college. Unfortunately it has since been abandoned and has fallen into a severe state of disrepair. It is slated for demolition at any time, as the land was split into eight parcels and sold off.

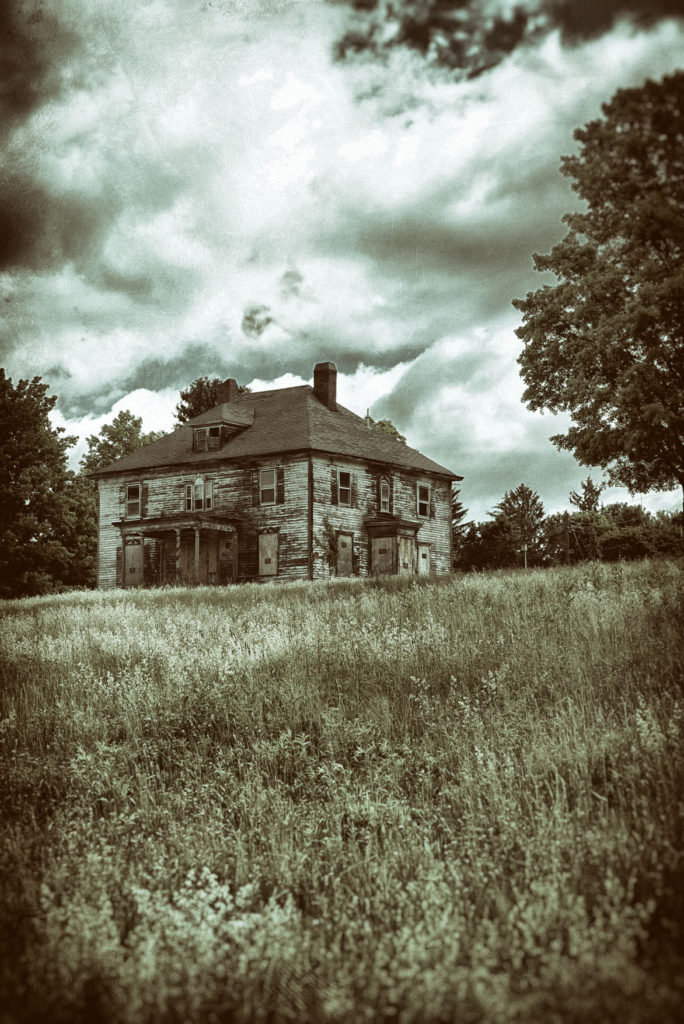
This ragged looking Walking Dead structure is, I believe, an annex to the school property.

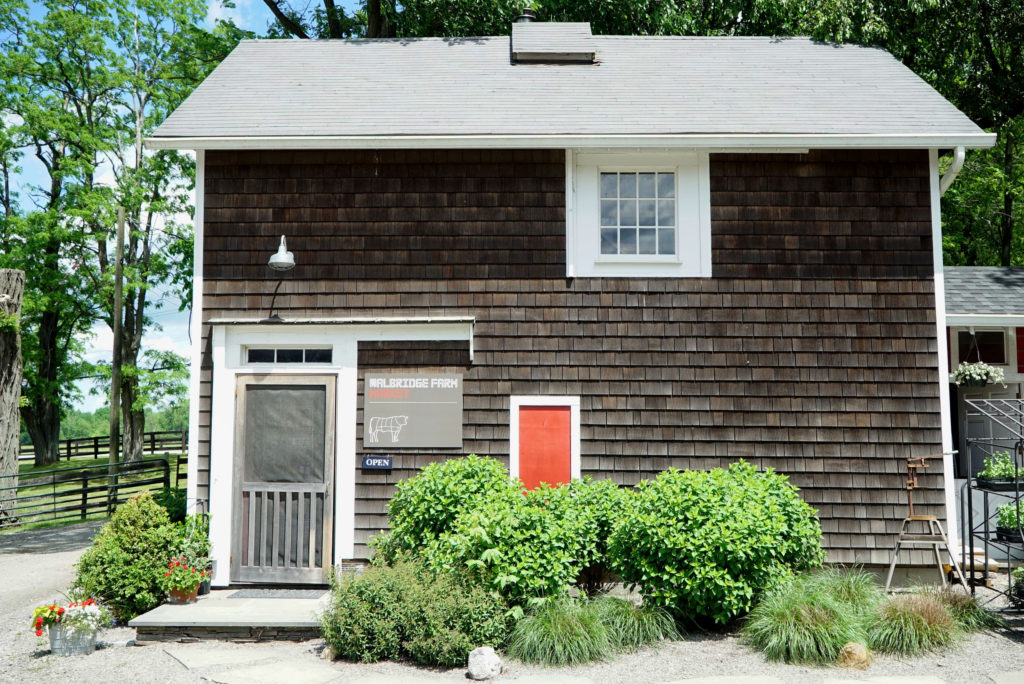
So we pulled up to Walbridge Farm and took in the grounds:
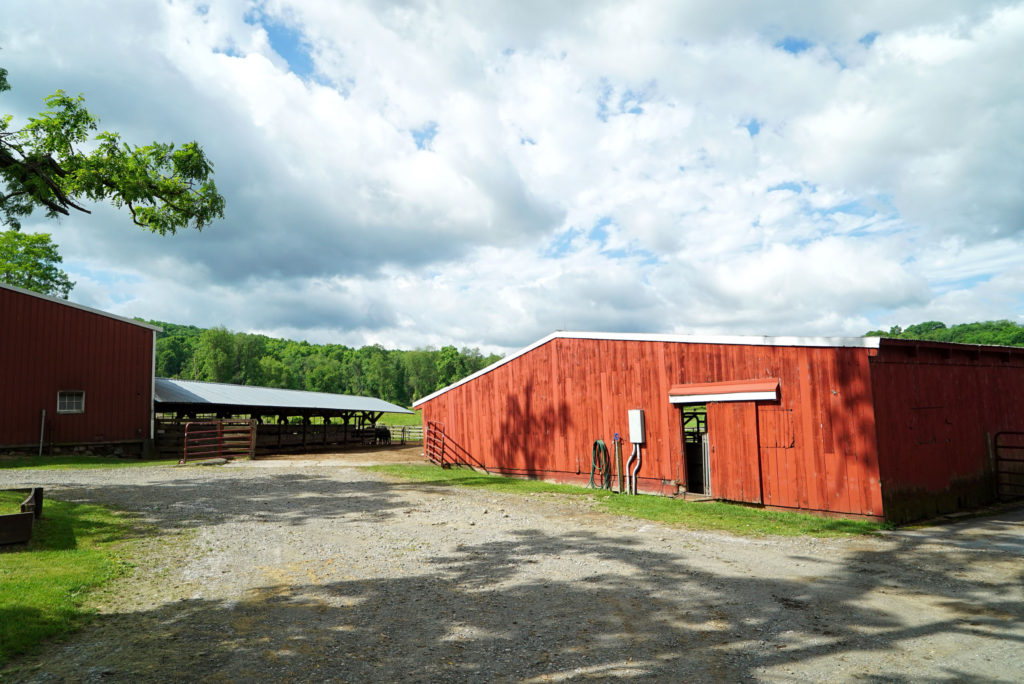
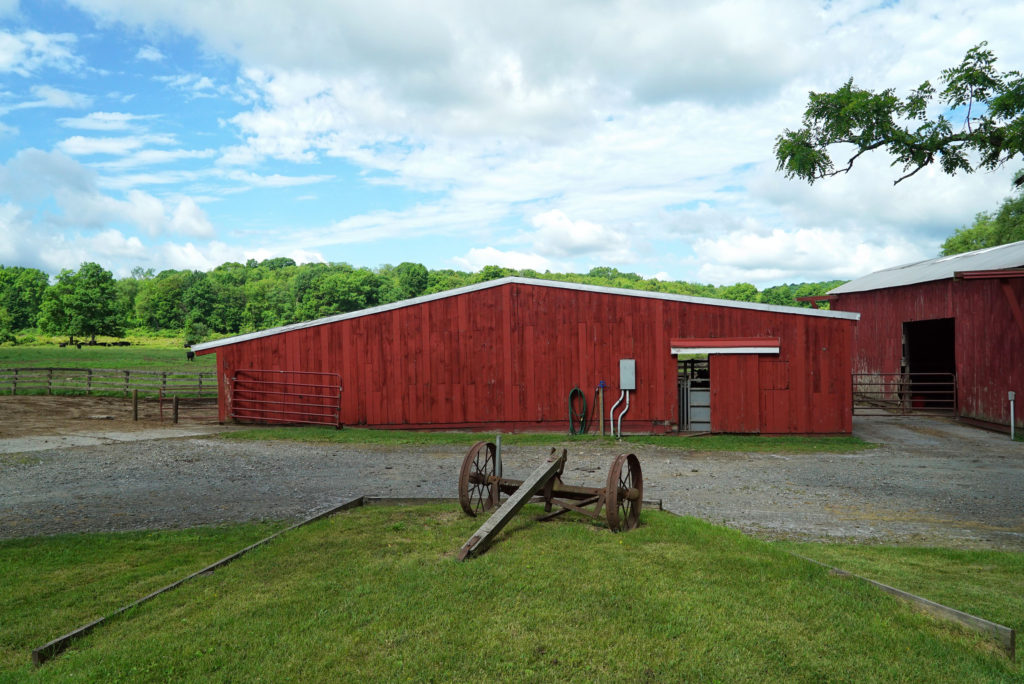






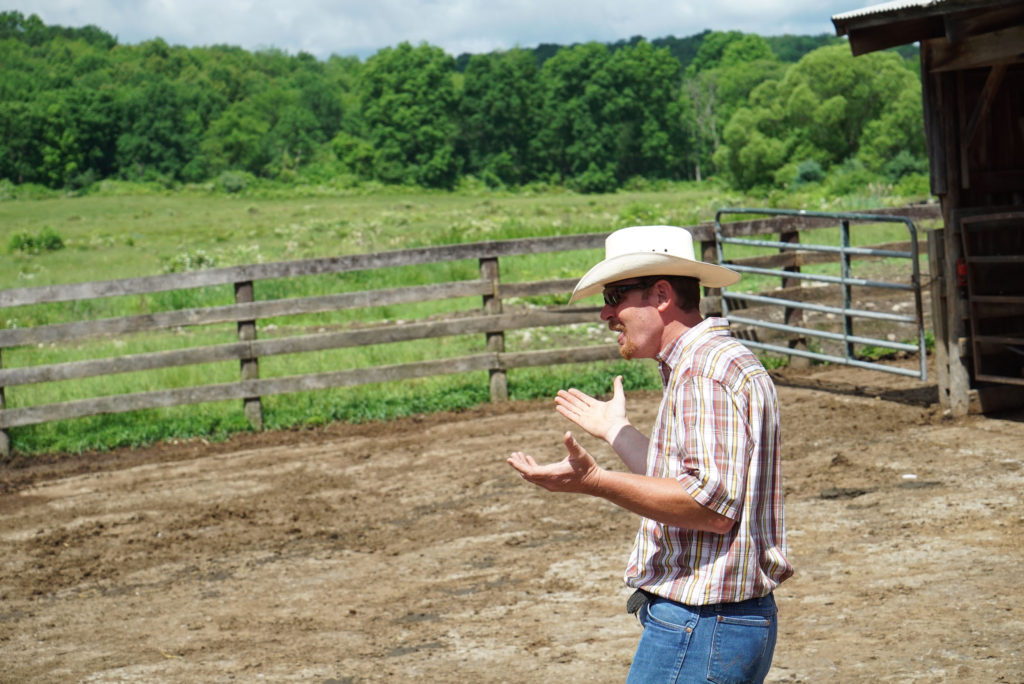
A few minutes later the tour began and the farm manager, Doug Giles, took us around to explain what happens at each structure on the farm.

The first thing we did was to “meet the meat.”
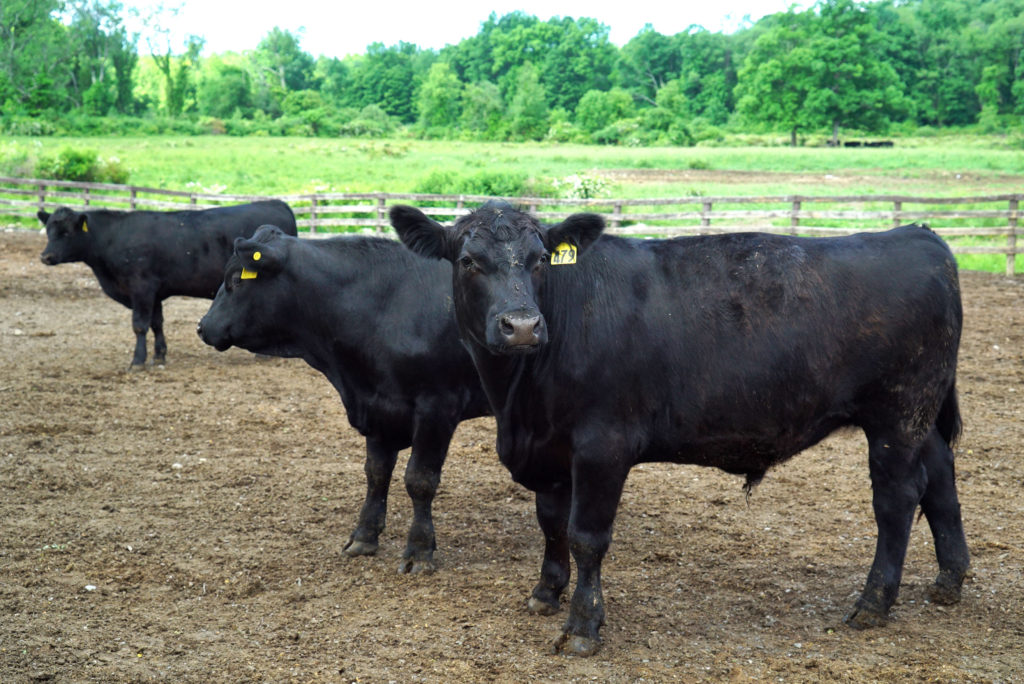
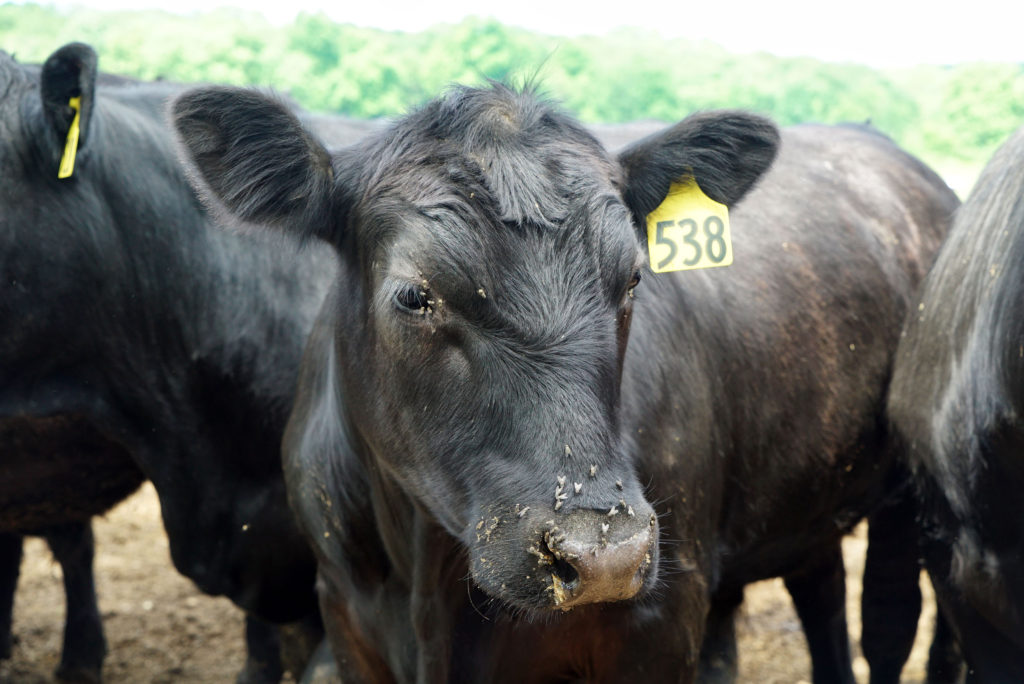
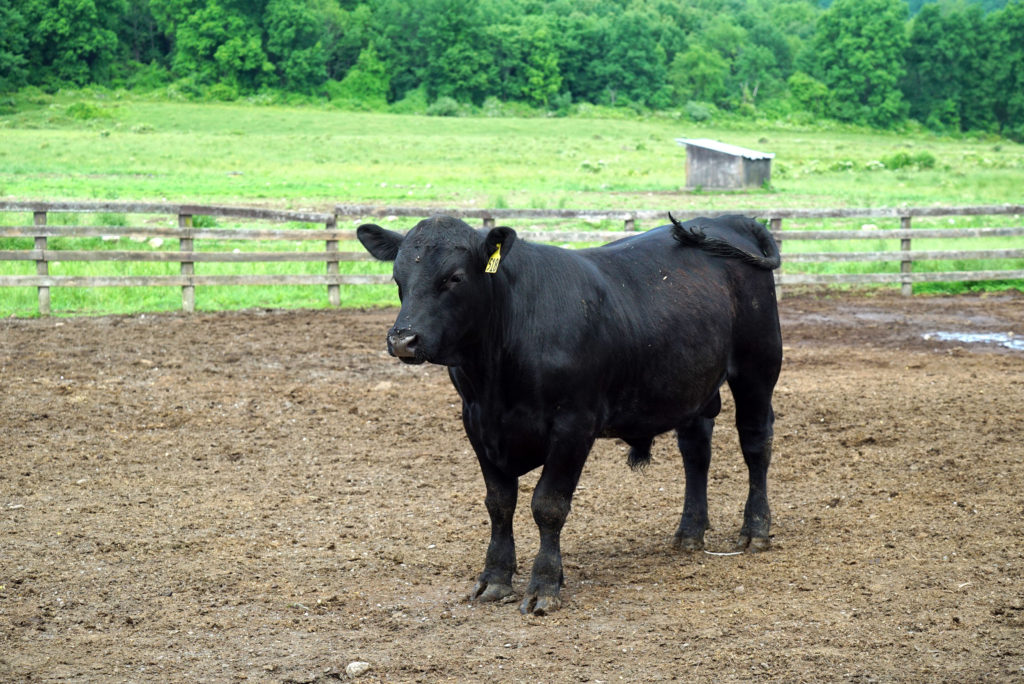




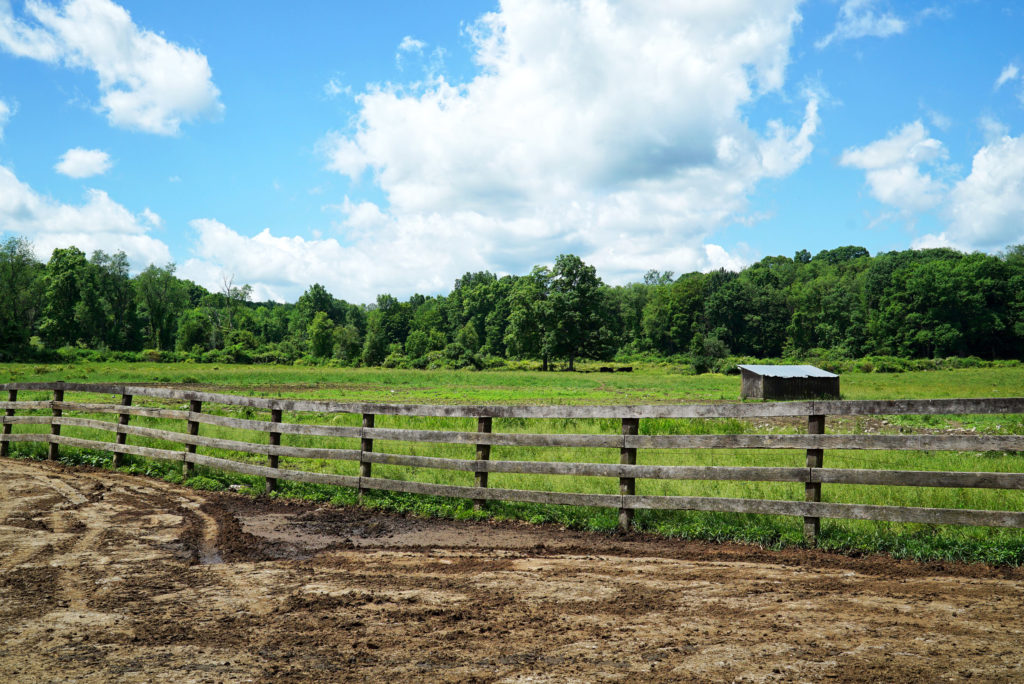
Walbridge is a sustainable Registered Black Angus farm. Their pasture raised Angus is grass fed and then grain finished. Their diet consists of corn, sunflower meal and hay – all grown on Walbridge Farm’s 900 acres plus the additional 700 acres that they lease and farm nearby. The large blue silos you see here store all that food.
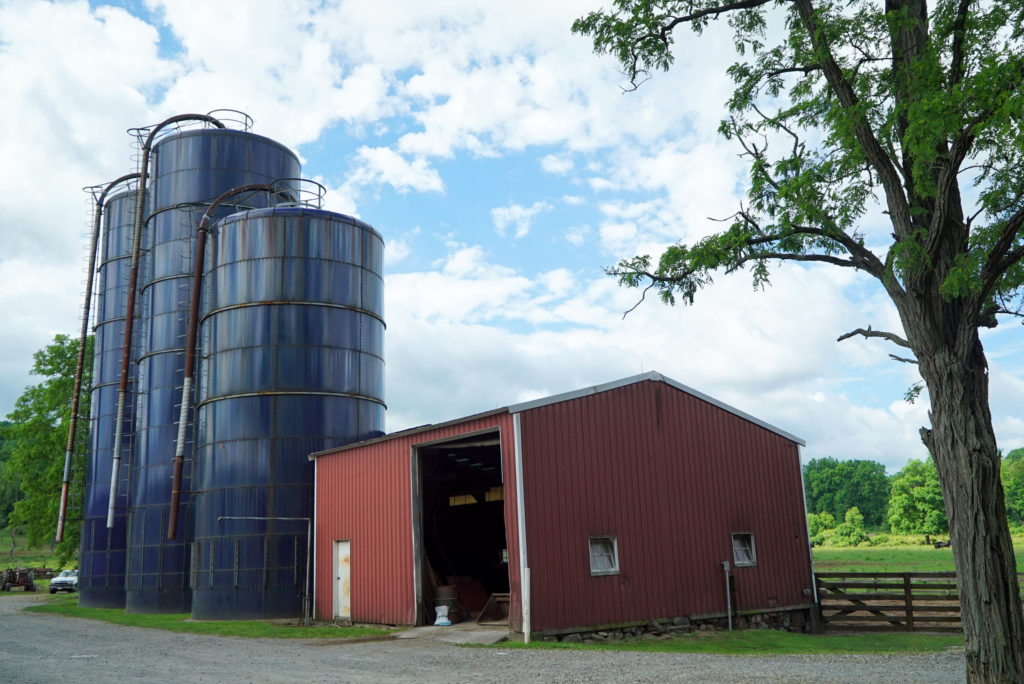

They don’t spray the fields with pesticides or insecticides, and their soils and water are tested yearly. That means the meat is pesticide free and non–GMO grain finished. In addition, their crops are rotated in order to care for the nutrients in the soils, and the cattle are moved throughout their fields in order to preserve the pastures.
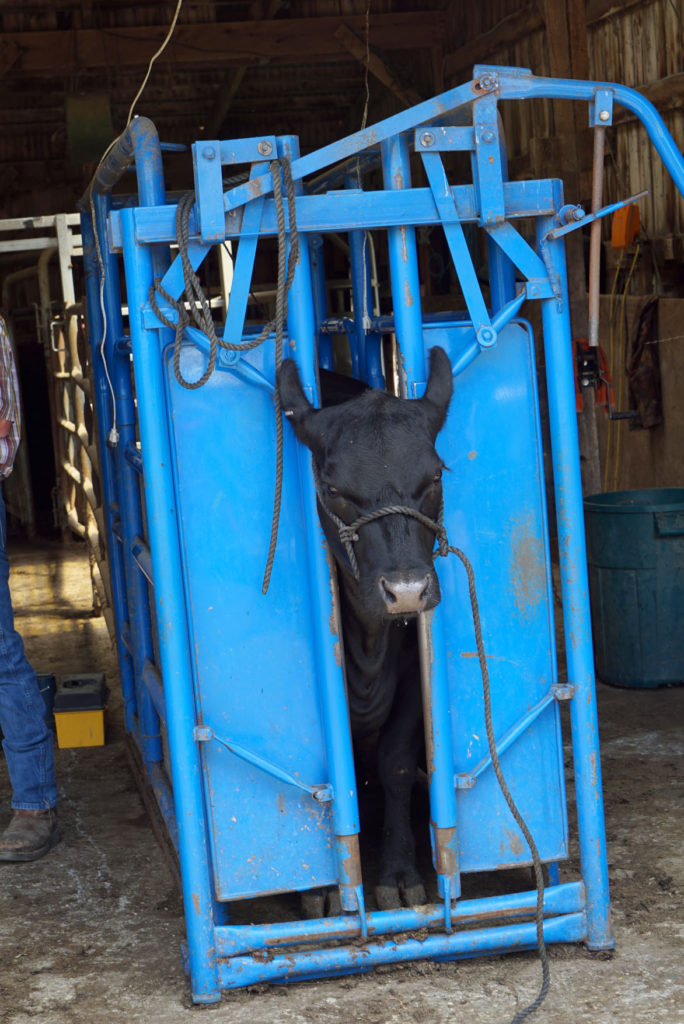
Doug then showed us how they monitor and control the cattle, in the event they have to tag them, inseminate them for calving, treat them for illness or get them ready to ship elsewhere.
In this barn, they can get corralled and directed into a single-file chute, where the animal can’t move away or hurt itself while being inspected or treated with vaccinations.
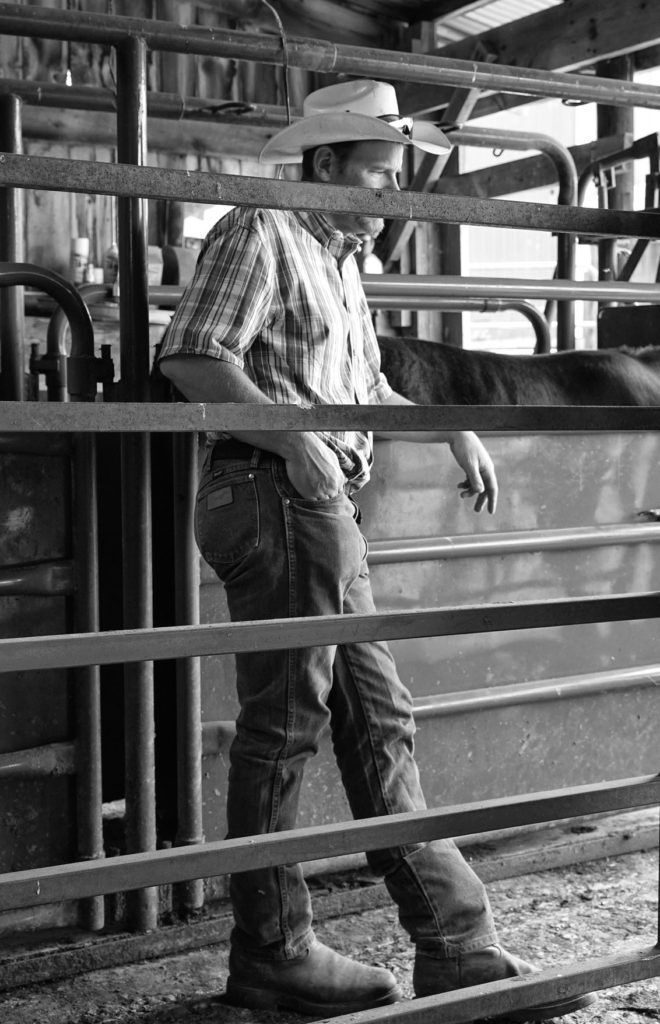


This beauty was off to a county fair to win some prizes.

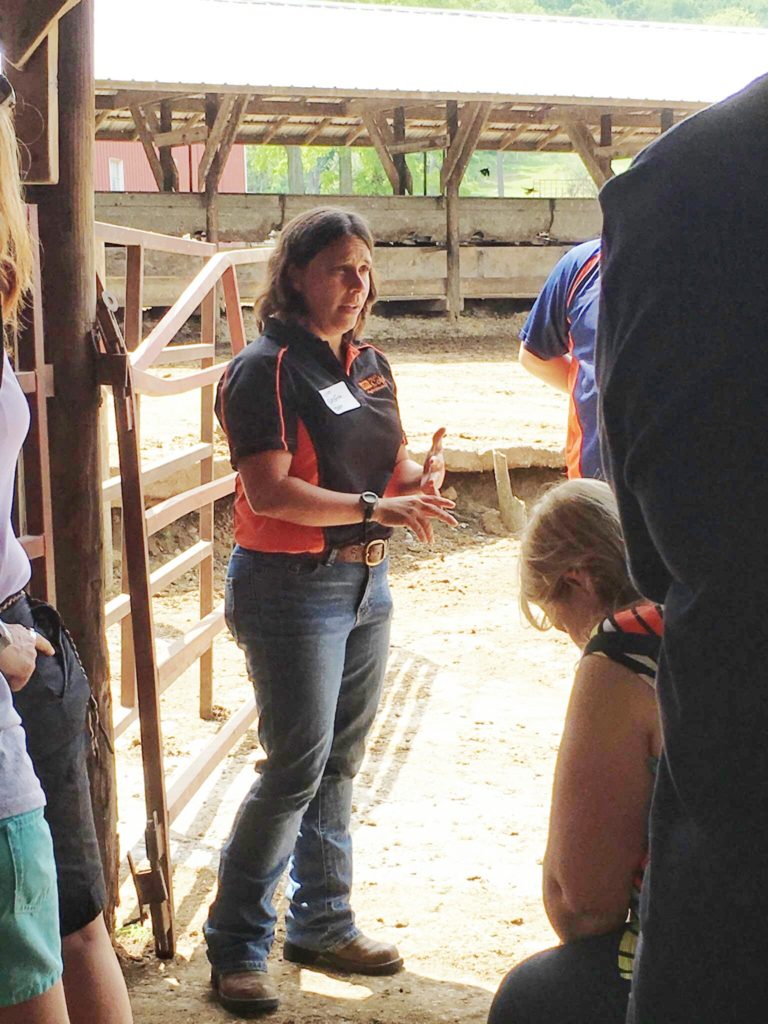
An animal specialist from SUNY Cobleskill, Assistant Professor Lynn Geoffroy, spoke next about antibiotics, animal nutrition and how animals are treated for illness.

If an animal is treated with antibiotics, by law the farm must wait a minimum of 28 days before it can be sent off and slaughtered for consumption. That’s how long it takes for the antibiotic to work its way out of the animal’s system. Vitamin hormones and ionophores are given to some cattle to aid in digestion and to prevent illness. These supplements are safe in terms of later human consumption, as they get completely metabolized by the animals. As such the ionophores are not as heavily regulated and don’t require rigorous documentation and paperwork like the use of antibiotics does.
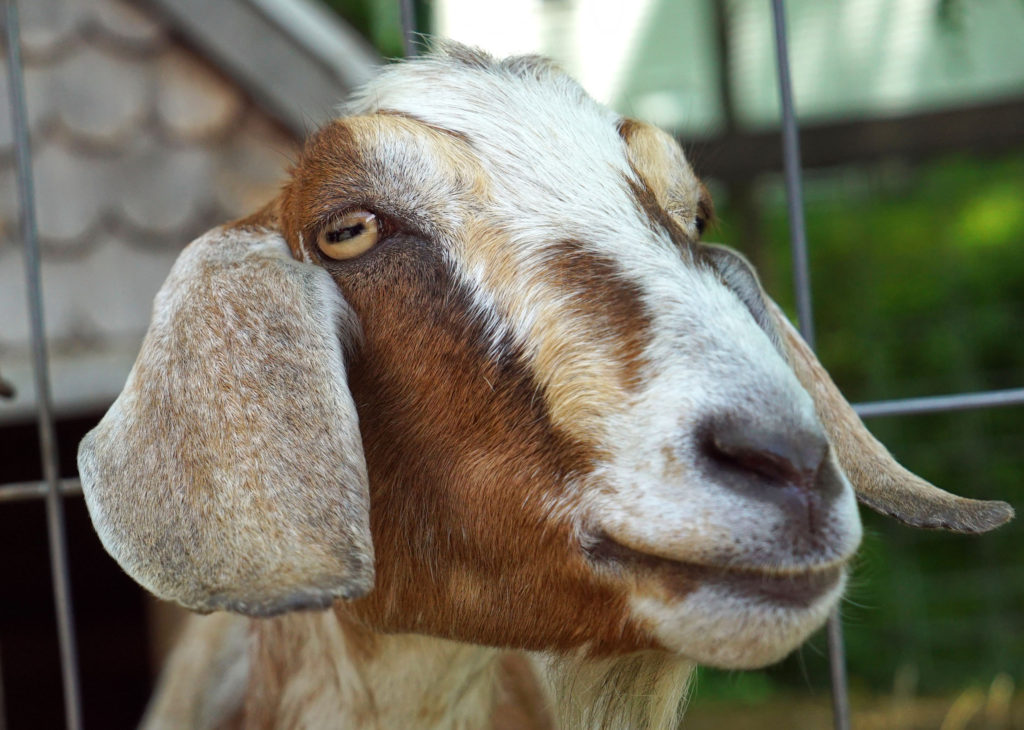
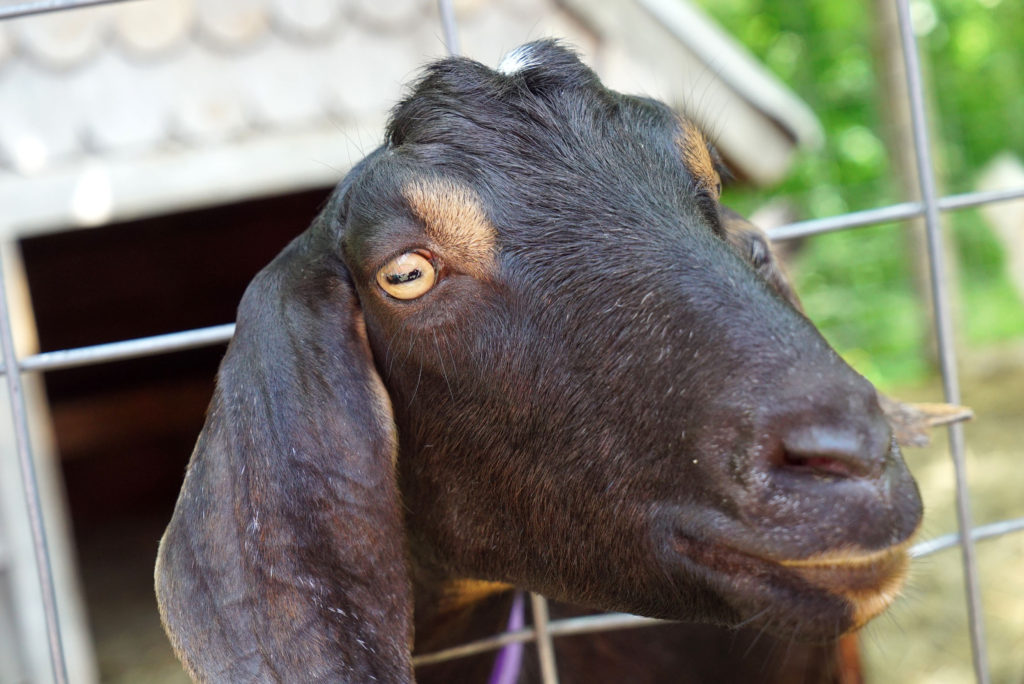
After the tour we had a few minutes to ourselves before lunch. We visited a trio of friendly goats, and checked out the farm stand store.





Walbridge also has over a hundred free-range egg-laying hens that eat an organic feed. Further, ten beehives are located throughout the acreage. Rich Honey Farm collects the honey harvest. Walbridge also works with Snowy Pass Farm to tap all of the maple trees on the property for syrup production. That’s total sustainability, and taking advantage of everything the land has to offer.
We sat down at our lunch table to a nice pile of swag for us to take home. Inside the oven mitt/pot holder was a plethora of info about beef, including recipes and even a knife sharpener.

And something that immediately interested me: a chart for taste testing notes and a scale for ranking various meat characteristics.
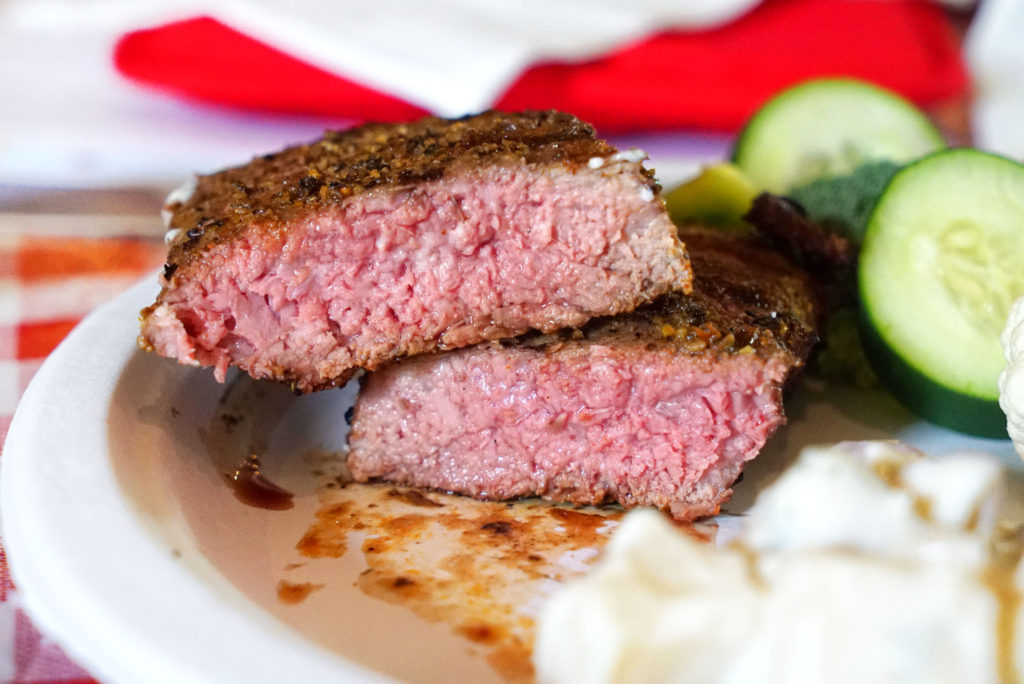
We sampled two meats, both were NY strip loin cuts. Jean O’Toole from the Beef Council didn’t tell us what we were looking for at first. She just asked which we liked better: A or B.
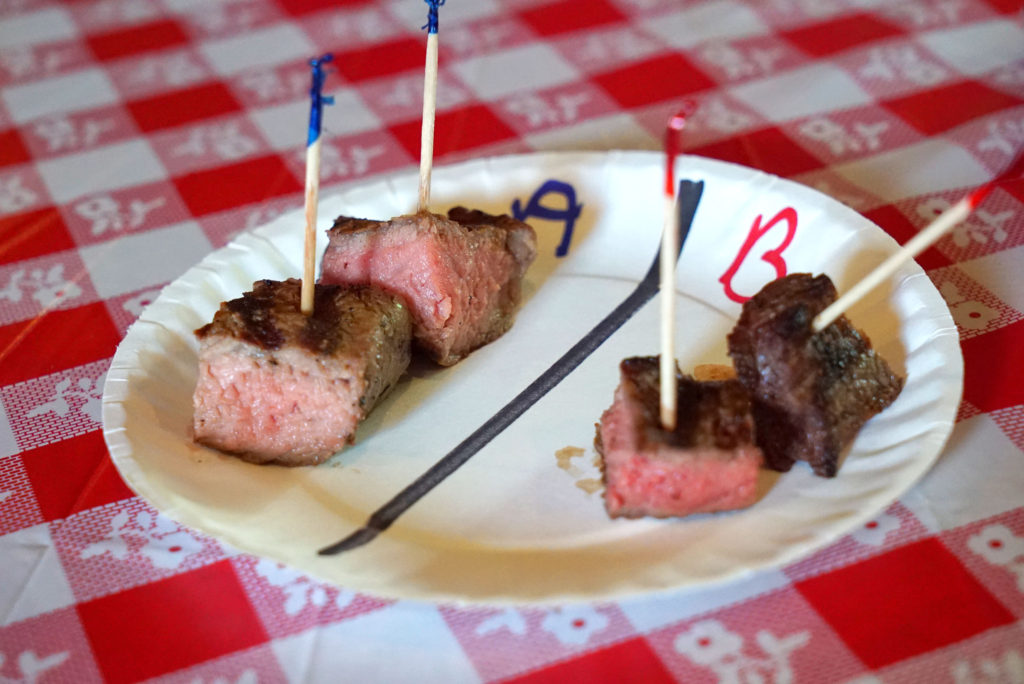

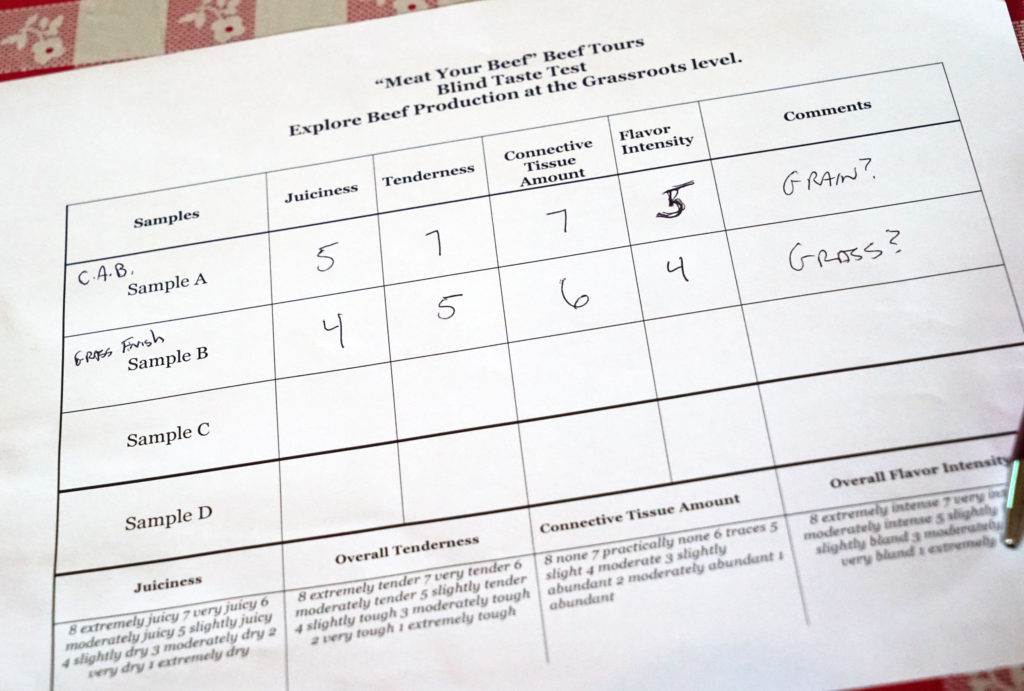
I preferred A. It was more tender, flavorful and juicy. Based on those characteristics, and that the texture of B was a bit more grainy and tough, I was guessing that A was grain-finished and B was grass-finished. It turns out I was correct (thank God – would have felt like an asshole if I didn’t get that right). Selection A was exactly the kind of beef that Walbridge produces: Certified Angus and grain-finished. Here are my notes from before the reveal:
After Jean announced the reveal, she passed around a plate of the steaks to show the difference in appearance and marbling between the two steaks.
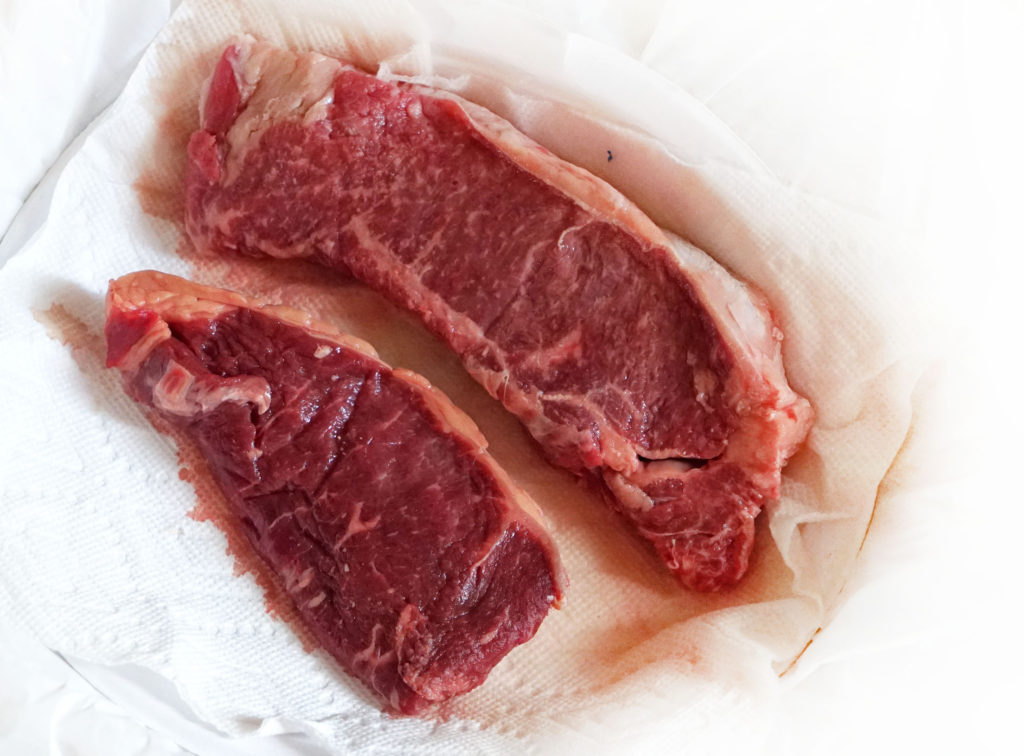

Grass finished animals are generally older when they go to slaughter, as it takes longer for those animals to pack on the fat and weight in order to get to a marketable production age. Grain finished animals fatten up faster and can go to market sooner. Older animals have darker red muscle flesh. So the left piece is grass-finished and the right piece is grain finished.
We also sampled some of this delicious cold-pressed sunflower oil by Hudson Valley. This stuff is actually made from the same sunflower seeds that the cows eventually eat at Walbridge Farm.
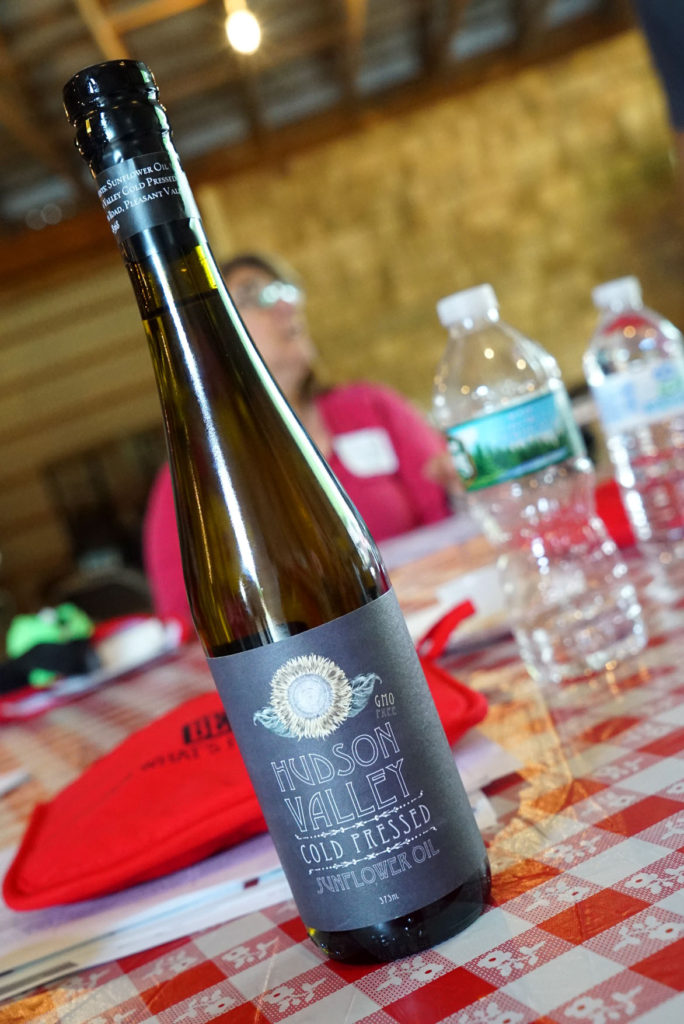

No chemicals are used when creating the oil, and the flavor is incredibly rich as a result of the more natural process. It even has a higher smoking point than olive oil, so better for certain types of frying. We actually picked up a bottle from the farm store. $15.
With that, we had all wet our appetites for a full lunch. Very simple and delicious: grilled strip loin, veggies, fruit and a cookie for dessert. I was a happy man.
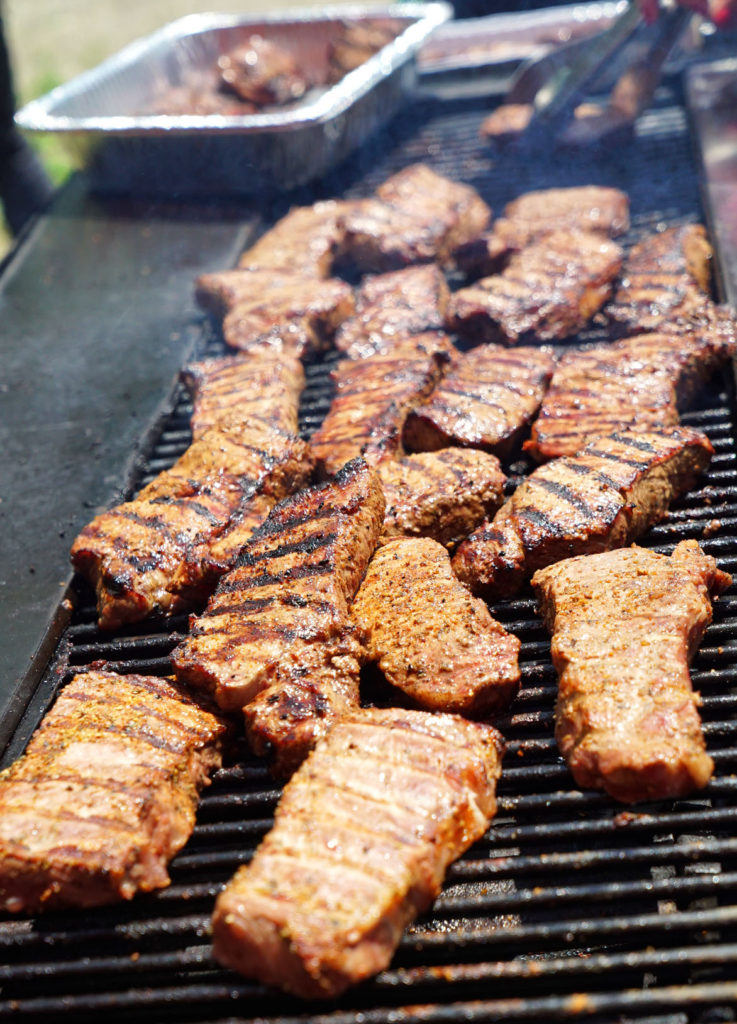



After lunch we were treated to a few lectures and presentations. The first was by nutritionist Cindy Phillips from the New York Beef Council. We learned about the differences in fat content between various types of beef produced from various types of feed finishing and farming techniques. She also discussed the many benefits from a diet that includes beef, dispelling many misconceptions in popular culture about beef being somehow bad for you.
The next presentation was about GMOs. Cornell Professor Dr. Margaret Smith gave a very unbiased and truthful look at the history of plant and animal selective breeding and the introduction of modern genetics into that field. While there is a lot of bad press on the subject of late, and lots of unknowns, many GMO products are completely benign. The industry shows great potential for helping farmers overcome the massive challenges they face in their business relating to crop/product yields, longevity and quality, as well as pest and weed control. However we did learn, essentially, that we are still learning a lot in this field of study, and that tests must be performed and caution must be taken each step of the way.
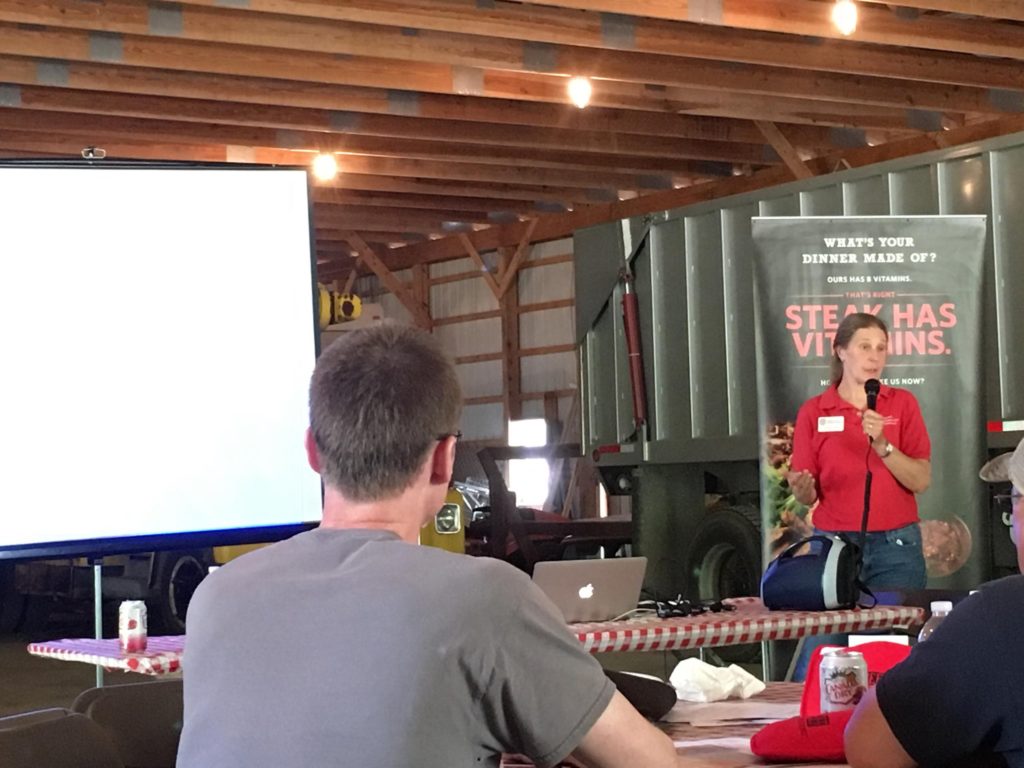

We also heard from SUNY Cobleskill Assistant Professor Dr. Jason Evans about the economics of the cattle industry. Growing up on a farm, he was able to discuss, with personal experience, the various hurdles and challenges within the field. With his educational background in economics, he also discussed possible ways that the industry can improve operations, going forward, given certain cycles and trends that he monitors.
The whole experience was very eye opening and informative. It dispelled many myths that you see floating around, and provided us with a lot of information to take away, with which we could continue researching and learning.
WALBRIDGE FARM MARKET
538 Route 343
Millbrook, NY 12545

